- Article Summary
-

In the world of investing, there are countless indices, but MSCI (Morgan Stanley Capital International) stands out as an indispensable resource for global investors. MSCI provides a variety of indices that cover stock markets worldwide and are widely used as benchmarks for investment decisions. In this article, we will dive deep into MSCI’s overview, key indices, ESG ratings, history, and applications.
Overview of MSCI
MSCI was founded in 1969 as a division of Morgan Stanley and is now an independent company that provides indices and research data to investors worldwide. MSCI’s indices are widely used to measure stock market performance and serve as benchmarks for portfolio construction by institutional investors and fund managers.
History of MSCI
MSCI (Morgan Stanley Capital International) has played a crucial role in the global financial market by providing indices and analytical tools that help investors make informed decisions. Below is a timeline of significant events in MSCI’s history:
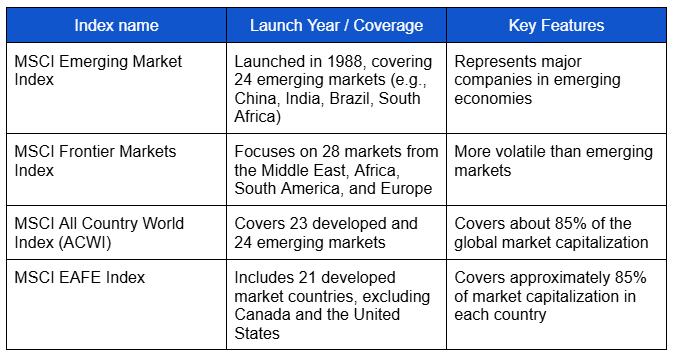
Key MSCI Indices
MSCI provides stock market indices covering different geographic regions and stock types (small-cap, mid-cap, and large-cap). These indices measure stock market performance and serve as benchmarks for ETFs (Exchange-Traded Funds) and other investment vehicles.
Assets Under Management (AUM)
As of December 31, 2023, a total of $15.6 trillion (T) in assets under management (AUM) were benchmarked to MSCI indices. Number of Indices Provided
MSCI offers over 280,000 indices (280K+), covering a wide range of markets and sectors.
This information highlights MSCI’s significant influence as a global index provider, playing a crucial role in shaping investment decisions worldwide.
What is ESG Rating?
In recent years, ESG (Environmental, Social, and Governance)-based investing has gained significant attention. MSCI provides ESG ratings that evaluate companies and countries based on these criteria, serving as a critical indicator for sustainable investments.
- Environmental (E): Greenhouse gas emissions, renewable energy usage
- Social (S): Labor practices, diversity, and community contributions
- Governance (G): Corporate governance structure, transparency, anti-corruption measures
MSCI’s ESG ratings help investors manage risks while identifying companies that prioritize sustainability.
How MSCI ESG Ratings Work
The MSCI ESG Ratings process involves several key steps to assess corporate sustainability effectively:
1. Identifying Key Issues
- MSCI identifies the most material ESG risks for each GICS® sub-industry or sector.
- These key issues are determined based on over 13 years of live track history.
2. Data Collection
- Corporate Disclosures: Company reports, filings, and sustainability disclosures.
- Alternative Data Sources: Media, academic research, NGO reports, regulatory and government data.
3. Technology and Human Expertise
- AI and advanced technologies enhance data collection and analysis.
- A team of 200+ analysts reviews, validates, and transforms data into meaningful insights.
4. Industry-Relative Scoring
- Companies are rated based on their exposure to ESG risks and their management relative to industry peers.
5. Continuous Update and Improvement
- Company ratings are updated throughout the year.
- The ESG Ratings model is reviewed and recalibrated annually, incorporating feedback from major investors.
MSCI ESG Ratings: Evaluating Corporate Sustainability
MSCI also provides ESG ratings, which assess a company’s sustainability and governance practices. These ratings help investors evaluate corporate risks and opportunities related to environmental, social, and governance factors.
Data Scope for ESG Ratings:
- 1,000+ data points analyzed for comprehensive ESG assessment
- 100,000 director profiles reviewed to evaluate governance structures
- 20 years of shareholder meeting results considered in the analysis
Scoring Criteria:
- Exposure Scores: Analyzes 80 business segments and geographic exposure metrics.
- Management Scores: Evaluates 270 policies, programs, performance, and governance indicators.
- Key Issue Scores & Weights: Assesses 35 governance risks and industry-specific key issues based on impact and the time horizon of risk or opportunity.
Understanding MSCI ESG Ratings
MSCI assigns ESG ratings to companies based on their performance relative to industry peers. The rating scale is as follows:
- Laggard (Low Rating): CCC, B
- Average: BB, BBB, A
- Leader (High Rating): AA, AAA
By analyzing key ESG issues, normalizing data across industries, and assigning weighted scores, MSCI provides investors with valuable insights into corporate sustainability.
Applications of MSCI
MSCI’s indices and ratings are used in various ways:
- Benchmarks for ETFs and Mutual Funds Many ETFs and mutual funds are designed to track MSCI indices, making them easily accessible to individual investors.
- Portfolio Construction Institutional investors and fund managers use MSCI indices as a foundation for building diversified portfolios and managing risk.
- Market Analysis and Performance Evaluation Investors compare their portfolio performance against MSCI indices to assess investment outcomes.
- ESG Investment Decisions
MSCI’s ESG ratings enable investors to focus on sustainable companies and industries, aligning investments with their values.
Support from Asuene
ASUENE provides support for ESG evaluation, offering solutions to help companies enhance their sustainability performance and meet global standards.
Let Asuene USA Inc. guide you in enhancing your MSCI ESG Rating and unlocking new opportunities in sustainable business practices.

