- Article Summary
-
Overview
Green spillover is the broader economic benefits triggered by sustainable practices and innovations. It is increasingly recognized as essential for sustainable economic growth. This article examines how green spillover fosters prosperity, exploring examples from Europe and the US to extract valuable lessons applicable globally. We aim to understand how strategic sustainability efforts can stimulate economic growth, generate employment, and enhance global competitiveness.
How Green Spillover Drives Economic Prosperity
Green spillover occurs when environmentally sustainable practices extend their benefits beyond their primary sector, improving efficiency, productivity, and innovation across the economy. These spillovers manifest in multiple ways:
- Innovation and Productivity: Sustainable technologies enhance overall economic productivity by promoting resource efficiency and cost reduction.
- Employment Creation: Renewable energy and sustainability sectors generate jobs that are resilient and geographically diverse.
- Investment Attraction: Regions prioritizing sustainability attract ESG-focused investors, amplifying capital inflows and economic resilience.
Lessons from Europe: Policy-Driven Green Spillover
Europe’s comprehensive regulatory framework has successfully positioned sustainability at the core of economic policy:
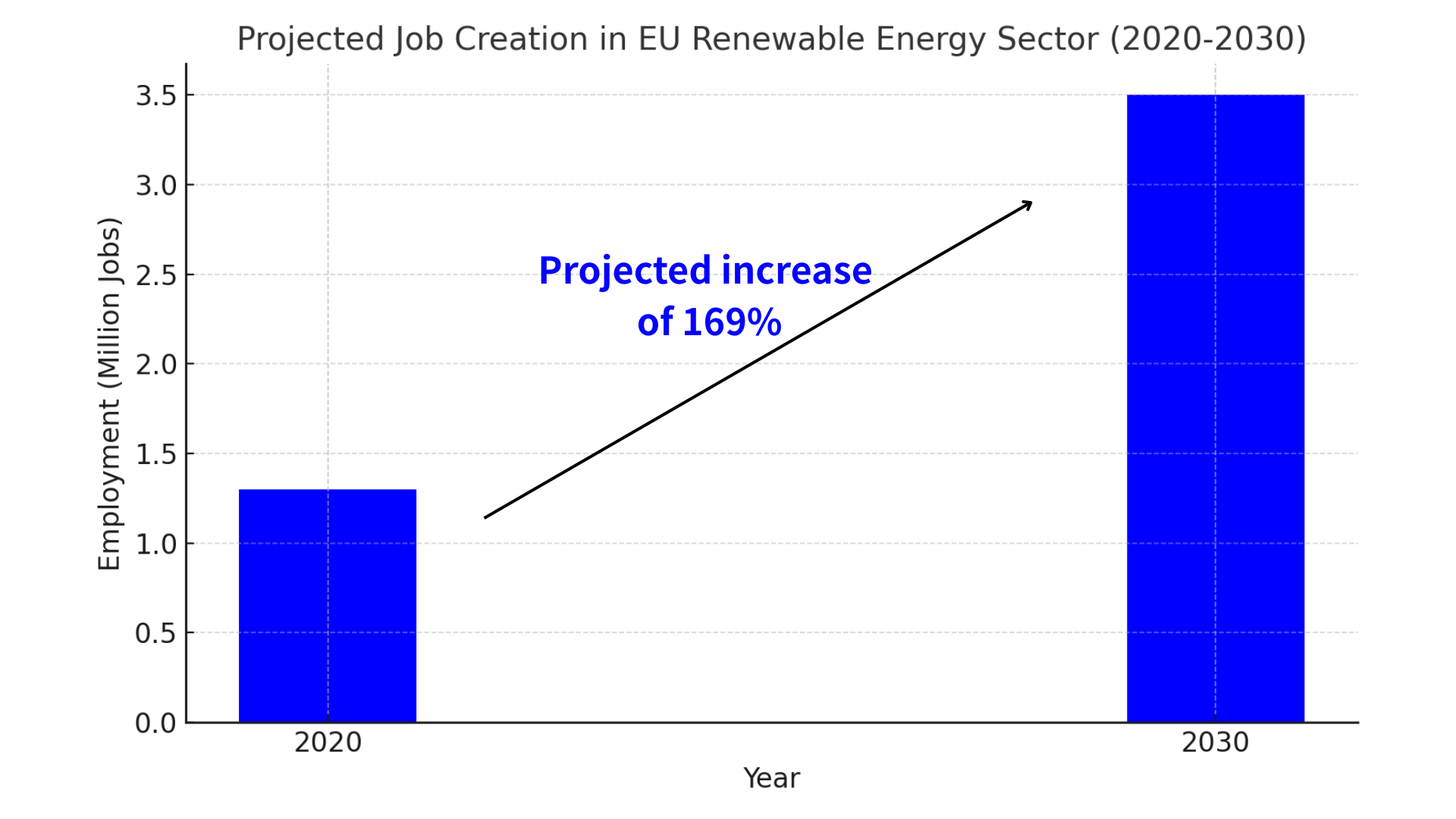
EU Green Deal: Launched in 2019, the EU Green Deal aims for Europe to become climate-neutral by 2050. This transformative policy package has driven substantial green investments totaling over €1 trillion by 2030. Employment in renewable energy sectors in the EU is projected to increase by approximately 30% between 2020 and 2030, driven significantly by the strategic initiatives outlined in the Green Deal. Clear policies like the Fit for 55 package set binding targets, driving innovation, supporting industries such as electric vehicles, solar, and wind energy, and significantly boosting employment and economic activity across multiple sectors.
Germany’s Energiewende: This ambitious energy policy fosters leadership in renewable technologies, resulting in increased export opportunities, technological advancements, and regional economic stimulation through job creation and infrastructure development.
Scandinavian Circular Economy Initiatives: These initiatives reduce waste and enhance resource efficiency, significantly lowering production costs and increasing competitiveness for local industries, thus stimulating regional economic resilience and prosperity.
Insights from the US: Innovation-Led Green Spillover
The US emphasizes private sector innovation as a primary driver for sustainability-driven economic benefits:
Silicon Valley and Austin: Both Silicon Valley and Austin have emerged as global leaders in clean technology and innovation. Silicon Valley hosts over 1,000 cleantech startups, forecasted to attract over $50 billion in investment between 2020 and 2030. Austin, renowned for its dynamic ecosystem, has become a magnet for cleantech and renewable energy companies, predicted to result in an increase of approximately 25% in employment within sustainable industries from 2022 to 2030. These cities provide favorable environments for innovation due to their strong venture capital presence, leading universities, and proactive local policies that foster collaboration among entrepreneurs, academia, and local governments.
Inflation Reduction Act (IRA): Through substantial financial incentives and subsidies, the IRA spurs investment in clean energy infrastructure, supporting extensive job creation and revitalizing local economies, particularly in historically under-invested regions.
Public-Private Partnerships: These partnerships facilitate rapid scalability and commercialization of sustainable technologies. Leveraging both government support and private-sector agility, they enable widespread deployment of innovations that significantly boost productivity and economic performance.

Bridging Strategies: Synergizing European and American Models
Each region offers complementary insights that, when combined, amplify global green spillover:
- Joint Research Initiatives: Collaborative research to accelerate innovation and commercialization.
- Regulatory Alignment: Harmonizing standards can scale sustainability practices more effectively.
- Global ESG Investment Frameworks: Coordinated investment strategies to enhance economic stability and sustainability globally.
Comparative Table:
| Aspect | Europe (Policy-Driven) | US (Innovation-Led) |
|---|---|---|
| Strengths | Regulatory clarity, systemic impact | Rapid innovation, scalability |
| Challenges | Regulatory rigidity | Market volatility, fragmented approaches |
| Mutual Learning Areas | Innovation acceleration, market flexibility | Regulatory effectiveness, systemic planning |
Conclusion
Unlocking economic growth through green spillover requires strategically integrating regulatory frameworks and innovation-driven approaches. Europe and the US provide complementary lessons on leveraging sustainability for economic prosperity. By synergizing these lessons globally, we enhance resilience, economic stability, and global competitiveness; creating pathways to a sustainable and economically vibrant future.
Why Work with ASUENE Inc.?
Asuene is a key player in carbon accounting, offering a comprehensive platform that measures, reduces, and reports emissions, including Scope 1-3. Asuene serves over 10,000 clients worldwide, providing an all-in-one solution that integrates GHG accounting, ESG supply chain management, a Carbon Credit exchange platform, and third-party verification.
ASUENE supports companies in achieving net-zero goals through advanced technology, consulting services, and an extensive network.


