- Article Summary
-
Overview
Life Cycle Assessment (LCA) is a method for measuring the environmental impact of a product from start to finish: from raw materials to disposal. As ESG (Environmental, Social, and Governance) reporting becomes more important, companies are using LCA to understand and reduce their environmental footprint. It helps identify where emissions and resource use occur across a product’s life, which is especially useful for tracking Scope 3 emissions and meeting new regulations.
What Is Life Cycle Assessment?
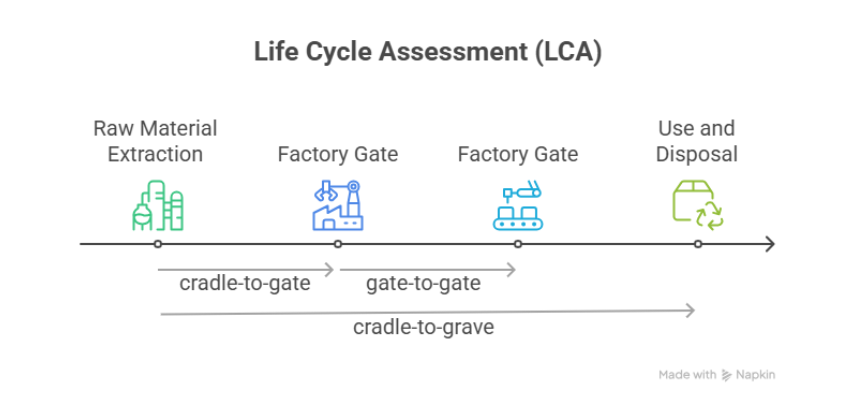
Life Cycle Assessment (LCA) is a methodological framework standardized under ISO 14040 and ISO 14044 for assessing environmental impacts associated with all the stages of a product’s life. These stages typically include: raw material extraction, material processing, manufacturing, distribution, use, and end-of-life (recycling, disposal, etc.).
LCA is categorized based on the scope of the life stages considered:
- Cradle-to-Gate: From raw material extraction to factory gate (before product use)
- Gate-to-Gate: A single value-added process within a product system
- Cradle-to-Grave: From raw material extraction through use and disposal
- Cradle-to-Cradle: A regenerative design where materials are reused indefinitely
The purpose of LCA is to move beyond intuitive or fragmented approaches to environmental performance and provide quantitative insights that align with ESG priorities.
It’s important to distinguish LCA from Carbon Footprint (CFP). While LCA evaluates a wide range of environmental impact categories (e.g., global warming potential, eutrophication, acidification, resource depletion, water use), CFP focuses exclusively on greenhouse gas emissions expressed as CO2-equivalents.
Why Cradle-to-Grave Matters in ESG Reporting
While cradle-to-gate analyses are valuable for internal optimizations and early-stage emissions accounting, cradle-to-grave assessments are more comprehensive and thus preferred in ESG disclosures. This is particularly relevant for Scope 3 emissions, which are the most difficult but significant part of corporate carbon footprints; sustainable finance, where investors demand full lifecycle impacts to assess long-term risks; and supply chain transparency, which helps identify hotspots across extended supply chains. Cradle-to-grave LCA provides decision-useful data that aligns with the goals of decarbonization, circular economy, and climate resilience.

Regulatory Landscape: U.S. and Europe in 2025
As of 2025, regulatory frameworks in both the United States and the European Union increasingly embed LCA methodologies:
- EU Corporate Sustainability Reporting Directive (CSRD): Mandates comprehensive environmental impact disclosure, including LCA data for product footprints
- EU Taxonomy: Requires cradle-to-grave environmental profiles for products to qualify as sustainable investments
- U.S. SEC Climate Disclosure Rule: Finalized in 2024, it encourages Scope 3 emissions reporting where material, indirectly pushing for LCA integration
- California Climate Corporate Data Accountability Act: Demands Scope 3 reporting for companies over a certain revenue threshold
These regulations emphasize transparency, comparability, and accountability across the value chain—a goal directly supported by cradle-to-grave LCA.
How Companies Can Implement LCA in ESG Strategy
Implementing cradle-to-grave LCA requires an integrated approach. Companies can use LCA software and databases such as Asuene to support data modeling and lifecycle analysis. Third-party verification ensures the credibility of results and compliance with ISO standards. Internally, cross-functional collaboration among ESG teams, procurement, operations, and R&D is crucial for effective execution. Companies can perform scenario modeling to explore the effects of product redesign, material substitution, and recycling. Many organizations are embedding LCA into digital ESG platforms with real-time data feeds, custom dashboards, and integration with financial KPIs to align sustainability goals with overall strategy.
Conclusion: From Compliance to Competitive Advantage
Cradle-to-grave LCA is more than a technical exercise; it’s a strategic asset. As ESG expectations evolve, the ability to quantify and communicate full lifecycle impacts becomes a differentiator in capital markets, regulatory landscapes, and customer relationships. Organizations that proactively adopt LCA methodologies not only enhance compliance but also unlock innovation, reduce risk, and demonstrate genuine sustainability leadership in a carbon-constrained economy.
Future-proofing ESG strategy requires data, depth, and disclosure; and cradle-to-grave LCA offers all three in a scientifically credible framework. For companies navigating 2025’s complex sustainability terrain, mastering LCA is not optional. It’s essential.
Why Work with ASUENE Inc.?
Asuene is a key player in carbon accounting and LCA, offering a comprehensive platform that measures, reduces, and reports emissions, including Scope 1-3, with expertise in decarbonization. Asuene serves over 10,000 clients worldwide, providing an all-in-one solution that integrates GHG accounting, ESG supply chain management, a Carbon Credit exchange platform, and third-party verification.
ASUENE supports companies in achieving net-zero goals through advanced technology, consulting services, and an extensive network.


