- Article Summary
-
Introduction: Why Environmental Product Declarations Matter Today
In a world increasingly focused on sustainability and climate accountability, transparency is no longer optional. Companies are under growing pressure from stakeholders, investors, and regulatory bodies to disclose the environmental impacts of their products and operations. This shift is particularly critical as organizations tackle the complexities of Scope 3 emissions and sustainable procurement.
Environmental Product Declarations (EPDs) have emerged as one of the most credible tools to address this demand. They offer standardized, third-party verified data on the environmental performance of products, based on a full life cycle assessment (LCA). Whether you’re a sustainability professional, procurement officer, or product manager, understanding EPDs is essential for aligning your organization with global ESG goals.
This article provides a comprehensive overview of EPDs, from how they are created to how they support ESG reporting, regulatory compliance, and product differentiation. Through visual aids and real-world examples, we aim to make the concept of EPDs practical and actionable for any sustainability-driven business.
What Is an EPD? Breaking Down the Concept
An Environmental Product Declaration (EPD) is a standardized document that provides quantifiable environmental data for a product based on its entire life cycle. It is governed by international standards such as ISO 14025 and EN 15804, which ensure consistency, reliability, and comparability across different product types and industries.
At its core, an EPD summarizes the results of a Life Cycle Assessment (LCA), which measures the environmental impacts associated with all stages of a product’s life, from raw material extraction to disposal. However, unlike a generic LCA report, an EPD is subject to strict rules called Product Category Rules (PCRs). PCRs define what to measure and how to report for a specific product type, ensuring that similar products can be fairly compared.
The process to develop an EPD includes:
- Conducting a Life Cycle Assessment (LCA): This involves data collection and impact assessment across stages like production, use, and disposal.
- Applying Product Category Rules (PCRs): These ensure that the methodology aligns with industry norms.
- Third-party Verification: An independent auditor reviews the EPD for accuracy and compliance.
- Registration and Publication: Verified EPDs are published in public databases such as EPD International or UL SPOT.
This rigorous approach ensures that EPDs provide trustworthy, science-based information.

The Business Case for EPDs in ESG Reporting
EPDs are more than technical documents. They play a strategic role in ESG and sustainability reporting. Their data-driven, transparent format makes them particularly useful for:
- Enhancing Scope 3 Emissions Accounting: EPDs give procurement teams precise data to measure upstream emissions.
- Supporting Green Procurement: Buyers can use EPDs to compare suppliers and select lower-impact products.
- Enabling Credible Communication: Companies can publicly demonstrate their environmental performance with confidence.
- Complying with Regulations: EPDs help meet regulatory and voluntary disclosure frameworks, such as the EU Green Deal or SEC climate disclosure proposals.
- Boosting Product Differentiation: Brands with EPD-certified products gain a competitive edge.
Below is a table comparing EPDs with other sustainability tools:
| Tool | Data Verified | Life Cycle Approach | Product-Specific | Publicly Available |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Environmental Product Declaration (EPD) | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Carbon Footprint Label | Sometimes | Often Partial | Yes | Sometimes |
| Environmental Labels (Type I) | Yes | No | Category-wide | Yes |
| Life Cycle Assessment (LCA) | No | Yes | Yes | No |
This table illustrates how EPDs strike the balance between depth, credibility, and accessibility.
EPDs Across Industries: Applications and Impact
EPDs are applicable across a wide range of industries and are rapidly becoming standard in sectors where environmental performance is under scrutiny. Here are some of the key areas:
Construction: Cement, steel, insulation, flooring, and other materials often carry EPDs to meet green building requirements. LEED and BREEAM certifications reward the use of EPD-backed materials.
Manufacturing: Electronics, machinery, and appliances use EPDs to demonstrate product-level emissions.
Consumer Goods: Packaging and apparel industries use EPDs to communicate sustainability to eco-conscious consumers.
As of mid-2024, there were over 10,000 valid EPDs registered with the International EPD® System. Below is a donut chart showing the distribution of EPDs by sector based on available data from global EPD databases:
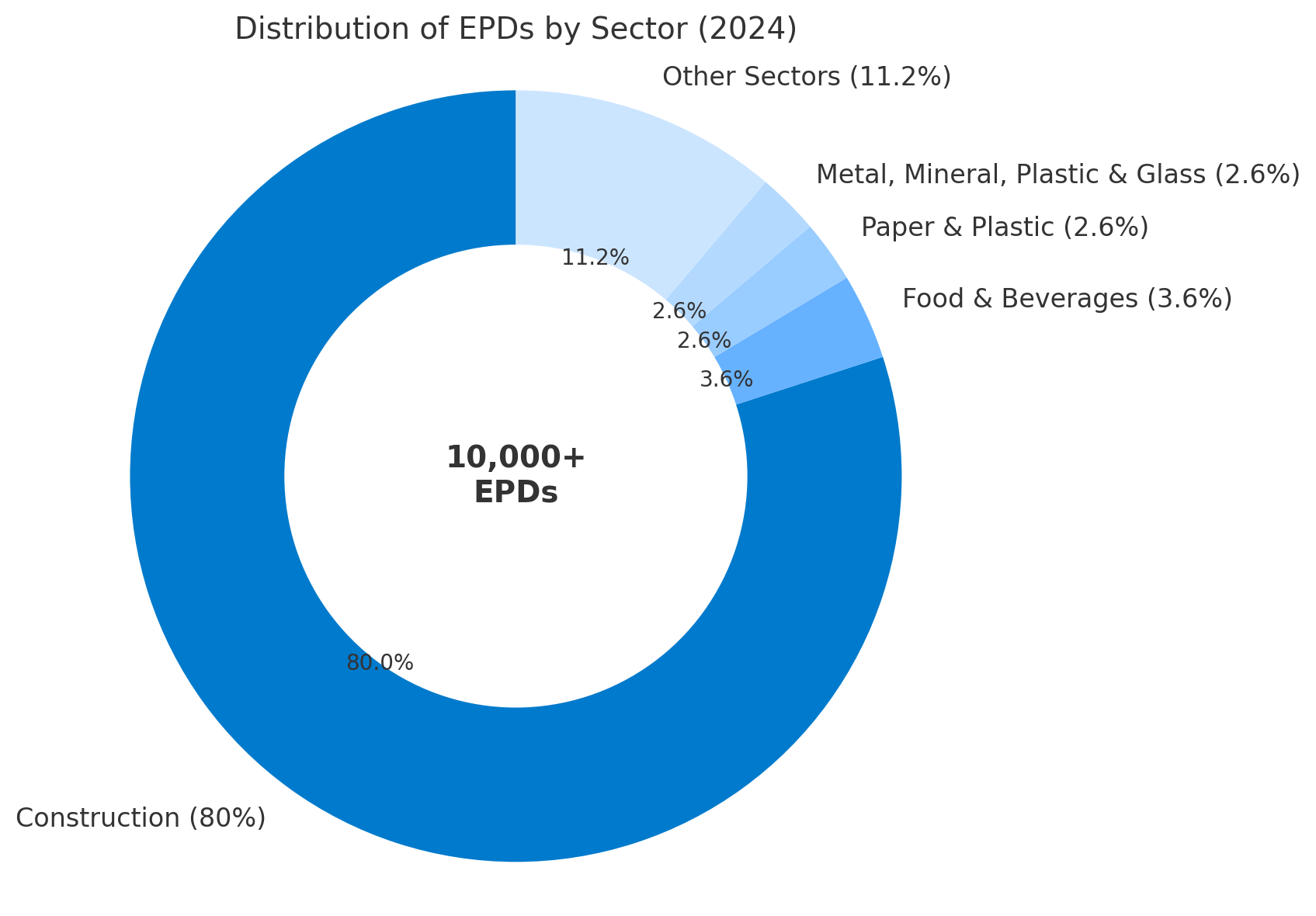
These figures demonstrate the growing adoption of EPDs, especially in carbon-intensive sectors.
Case in point: Skanska, a global construction firm, has integrated EPDs into its procurement strategy to select low-carbon concrete, achieving substantial emission reductions across its project portfolio.
Conclusion: Moving Toward a Transparent, Data-Driven Future
As sustainability expectations continue to rise, Environmental Product Declarations provide a crucial tool for credible, data-driven environmental disclosure. They help companies move beyond vague marketing claims and embrace a standardized, science-based approach to sustainability.
By adopting EPDs, businesses can gain clarity on the environmental impacts of their products at the individual level, enabling more accurate and transparent reporting. This understanding allows organizations to make better procurement choices that prioritize lower-impact options, ultimately contributing to a more sustainable supply chain. EPDs also support companies in meeting the increasing demands of regulatory compliance, helping them stay ahead of emerging policies and frameworks. Furthermore, they provide a strong foundation for enhancing ESG reporting by introducing standardized, science-based metrics that can be communicated with confidence to stakeholders.
Looking ahead, the role of EPDs will only grow. Innovations such as digital EPDs, blockchain verification, and AI-assisted LCA modeling promise to make environmental reporting even more robust and scalable. For companies serious about sustainability, now is the time to integrate EPDs into their strategy and lead with transparency, precision, and integrity.
Why Work with ASUENE Inc.?
Asuene is a key player in carbon accounting, offering a comprehensive platform that measures, reduces, and reports emissions. Asuene serves over 10,000 clients worldwide, providing an all-in-one solution that integrates GHG accounting, ESG supply chain management, a Carbon Credit exchange platform, and third-party verification.
ASUENE supports companies in achieving net-zero goals through advanced technology, consulting services, and an extensive network.


