- Article Summary
-
As global supply chains grow in complexity, the ethical sourcing of raw materials has become a core ESG concern. At the center of this discussion are conflict minerals: tin, tungsten, tantalum, and gold (commonly known as 3TG), which are often mined in regions plagued by armed conflict and human rights abuses, particularly the Democratic Republic of Congo (DRC) and adjoining countries.
For companies operating in or supplying to the EU and the US, addressing conflict minerals is no longer a reputational issue alone—it is a legal and regulatory requirement. This article examines how businesses can comply with regulations like the EU Conflict Minerals Regulation and the U.S. Dodd-Frank Act (Section 1502), while embedding due diligence and traceability practices into their supply chain strategies.
Understanding the Scope: What Are Conflict Minerals?
Conflict minerals refer to 3TG elements extracted under conditions that directly or indirectly finance armed groups, contribute to forced labor, or cause environmental destruction. These materials are widely used in:
- Electronics (semiconductors, batteries, circuit boards)
- Automotive (engine components, airbags)
- Jewelry and luxury goods
- Aerospace and defense
The global push to regulate 3TG began with the U.S. Dodd-Frank Act (2010), which requires public companies to disclose the origin of these minerals. The EU followed suit with its Conflict Minerals Regulation, which came into effect in January 2021, focusing on importers of raw materials and smelters/refiners.

Common Uses of Conflict Minerals by Industry
| Mineral | Typical Use | Industry |
|---|---|---|
| Tin | Solder in electronics | Electronics, Auto |
| Tungsten | Hardening metal, tools, mobile phones | Engineering, Defense |
| Tantalum | Capacitors in phones/laptops | Tech, Aerospace |
| Gold | Circuitry, connectors, jewelry | Electronics, Luxury |
Regulatory Landscape: EU vs. U.S. Requirements
Both the EU and U.S. have implemented frameworks to curb the flow of conflict minerals, but their focus differs:
- U.S. Dodd-Frank (Section 1502): Applies to U.S.-listed companies manufacturing products containing 3TG. Requires annual Form SD filings and independent audits.
- EU Conflict Minerals Regulation: Applies to EU-based importers of raw 3TG materials above certain thresholds. Requires due diligence aligned with OECD Guidance.
Unlike the U.S., the EU regulation currently does not apply to downstream manufacturers or retailers—though this may change with the upcoming Corporate Sustainability Due Diligence Directive (CSDDD).
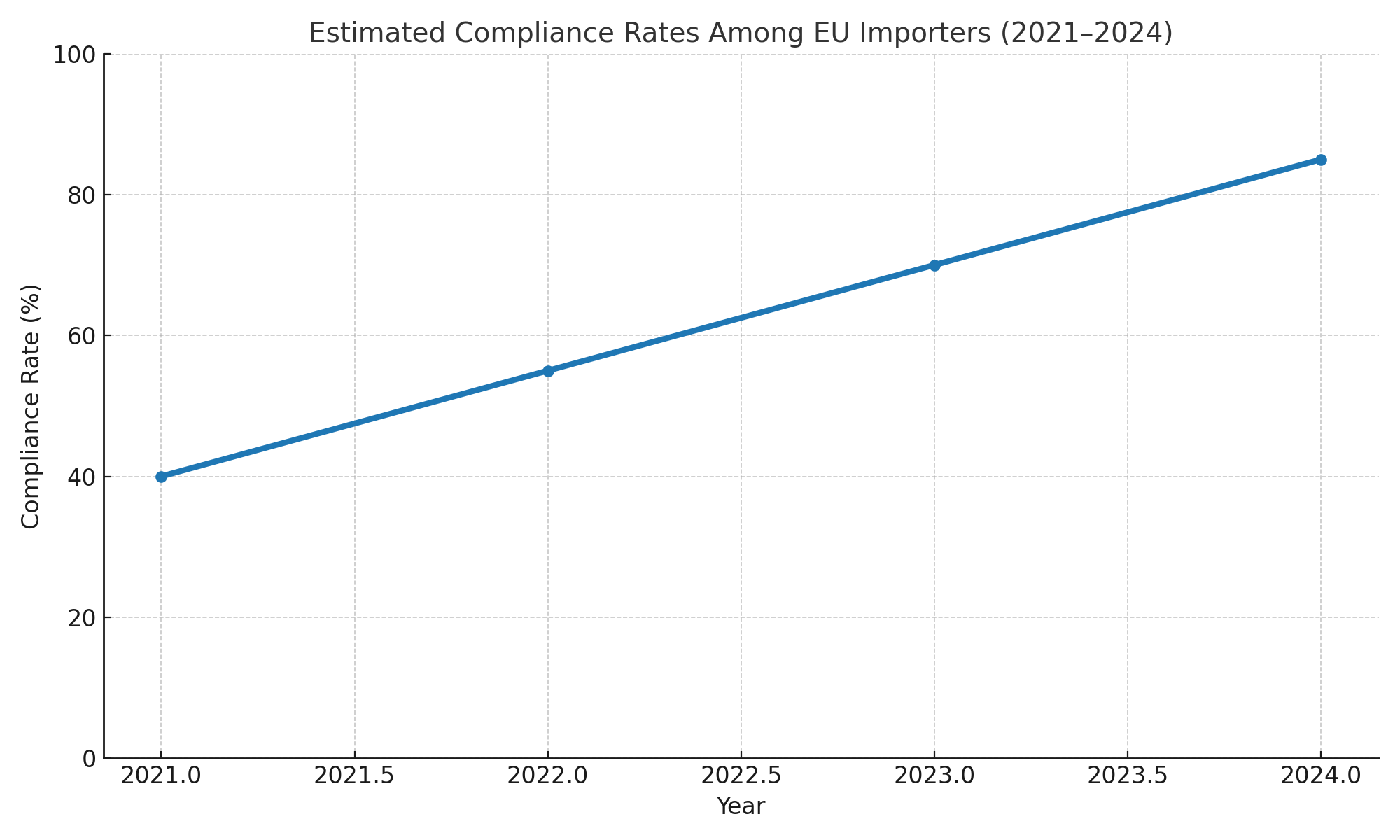
Estimated Compliance Rates Among EU Importers (2021–2024)
Implementing Conflict Minerals Due Diligence
Effective due diligence involves five key steps based on the OECD Due Diligence Guidance:
- Establish strong company management systems
- Identify and assess risks in the supply chain
- Design and implement a strategy to respond to risks
- Conduct third-party audits of supply chain due diligence
- Report annually on due diligence efforts
Best practices include:
- Supplier codes of conduct including 3TG sourcing policies
- Traceability systems using blockchain or QR tracking
- Participation in industry initiatives (e.g., RMI, iTSCi, LBMA)
- Whistleblower channels and grievance mechanisms
Technology and Transparency in Mineral Sourcing
Digital tools are enabling unprecedented levels of supply chain visibility:
- Blockchain-based platforms can trace minerals from mine to manufacturer.
- Digital Product Passports (DPPs) in development under EU legislation will standardize traceability.
- Geospatial analysis and satellite imagery help monitor illegal mining operations.
Case in point: Intel and Apple have integrated supplier auditing platforms and conflict-free sourcing programs verified by third parties, dramatically improving transparency and trust.
Conclusion
Managing conflict minerals is not just about regulatory compliance—it’s about ethical sourcing, supply chain resilience, and brand integrity. As the EU and global frameworks evolve, proactive companies will be those that move beyond minimum requirements and build robust, transparent, and traceable sourcing systems.
By embedding conflict minerals due diligence into ESG strategies, businesses can reduce risk, meet stakeholder expectations, and support responsible resource extraction in vulnerable regions.
Why Work with ASUENE Inc.?
Asuene is a key player in carbon accounting, offering a comprehensive platform that measures, reduces, and reports emissions, including Scope 1-3, with expertise in decarbonization. Asuene serves over 10,000 clients worldwide, providing an all-in-one solution that integrates GHG accounting, ESG supply chain management, a Carbon Credit exchange platform, and third-party verification.
ASUENE supports companies in achieving net-zero goals through advanced technology, consulting services, and an extensive network.


