- Article Summary
-
Overview
As the world confronts the mounting climate crisis, renewable electrification stands out as a crucial strategy for achieving sustainable energy transformation. Electrification, coupled with renewable energy integration, is essential for significantly reducing global carbon emissions and creating resilient, future-proof energy systems. This article explores the accelerating trend towards renewable electrification, analyzing key drivers, sector-specific developments, recent regulatory shifts, and potential challenges and solutions.
Why Electrification Matters
Electrification is essential to the global shift toward sustainability because it directly reduces reliance on fossil fuels. Electric power, especially when sourced from renewable energy, is cleaner, more efficient, and easier to integrate into modern energy infrastructures. Key benefits include enhanced energy efficiency, greater integration of renewables, and significant reductions in greenhouse gas emissions.
Recent studies indicate that comprehensive electrification strategies could reduce global emissions by as much as 70% by 2050, assuming parallel growth in renewable energy production.
Policy Drivers of Electrification (Post-2025 Regulations)
Since 2025, both the US and Europe have introduced specific regulations to boost renewable electrification.
In the United States, policies such as the Inflation Reduction Act (IRA) continue to offer substantial tax incentives for renewable energy and electric vehicles. Additionally, the Environmental Protection Agency’s strengthened vehicle emission standards aim to significantly reduce emissions from transportation. The Federal Energy Regulatory Commission has also simplified processes to connect renewable energy projects to the power grid and introduced reforms to improve grid planning and infrastructure.
In Europe, the updated Renewable Energy Directive (RED III) sets ambitious targets for renewable energy use, including specific goals for transportation, heating, cooling, and industrial sectors. The directive mandates that 42.5% of overall energy must come from renewable sources by 2030. Furthermore, streamlined permitting processes introduced through initiatives like REPowerEU facilitate quicker development of renewable infrastructure. The UK’s Great British Energy Act 2025 further reinforces these efforts by establishing a public entity to accelerate renewable energy generation and infrastructure development.
These policy frameworks have collectively driven significant investment and progress toward electrification goals in both regions.

Sector Spotlight
Transportation, industry, and building sectors are pivotal to the global energy transition due to their substantial emissions.
Transportation:
The global market for electric vehicles (EVs) is rapidly expanding, driven by consumer demand, improved affordability, and robust policy support. Investments in charging infrastructure are scaling significantly, ensuring wider accessibility and reliability for consumers. Concurrently, advancements in battery technology, such as improvements in energy density and reductions in manufacturing costs, have substantially increased EV adoption and reduced transportation emissions.
Industry:
Heavy industries, such as steel, chemicals, and manufacturing, are shifting towards electrification. Electrified processes like electric arc furnaces in green steelmaking drastically lower emissions compared to traditional methods. Electric heating technologies further reduce fossil fuel use, offering sustainable and cost-effective industrial solutions aligned with decarbonization goals.
Buildings:
The building sector is increasingly adopting electrification solutions to reduce emissions. The shift from gas heating systems to electric heat pumps and electric water heaters substantially decreases fossil fuel consumption. Energy efficiency improvements, combined with electrification strategies such as smart energy management and integrated solar systems, enable buildings to significantly reduce their carbon footprint while ensuring greater energy resilience.
Progress Comparison: Renewables vs. Electrification
Both renewable energy adoption and electrification are well underway, though their progress is uneven. Renewable energy adoption, particularly solar and wind, has seen rapid acceleration globally, steadily increasing its share of power generation. Electrification, although already more advanced in some regions, is progressing more gradually, with significant variations between countries and sectors. This reflects the differing stages of technological maturity, policy support, and infrastructure availability between the two pathways.
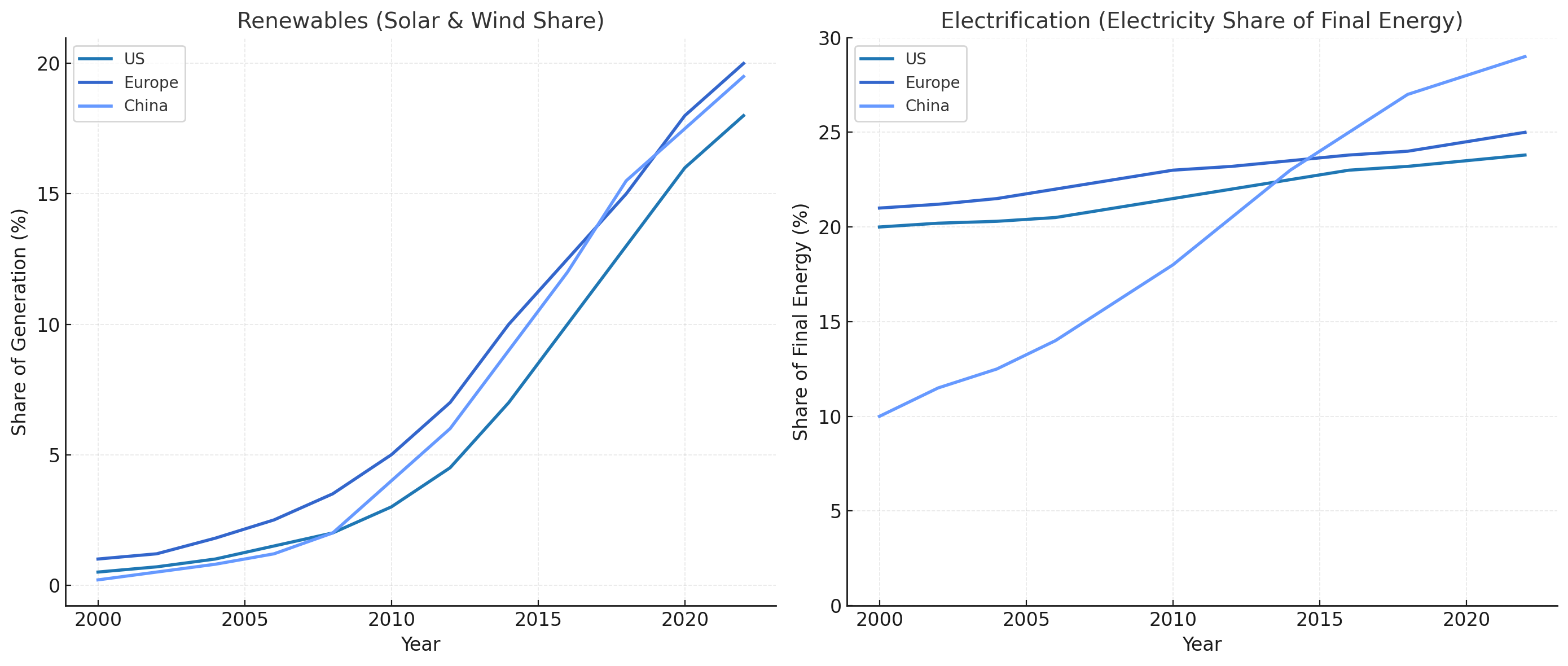
Challenges and Solutions: Integrating Renewables with Electrification
Despite clear benefits, significant challenges persist, including grid stability due to renewable energy variability, limitations in energy storage technology, and the need for extensive infrastructure upgrades.
Solutions involve investing in advanced energy storage technologies like flow batteries and hydrogen systems, adopting smart grid technologies for improved grid management, and implementing policy incentives to encourage public-private collaboration in infrastructure development.
Conclusion
Renewable electrification represents a crucial pathway toward achieving a sustainable global energy future. While challenges remain, ongoing policy support, technological advancements, and targeted sectoral actions continue driving progress. Accelerating renewable electrification is essential to meet global climate objectives and build a resilient, renewable-powered world.
Why Work with ASUENE Inc.?
Asuene is a key player in carbon accounting, offering a comprehensive platform that measures, reduces, and reports emissions, including Scope 1-3. Asuene serves over 10,000 clients worldwide, providing an all-in-one solution that integrates GHG accounting, ESG supply chain management, a Carbon Credit exchange platform, and third-party verification.
ASUENE supports companies in achieving net-zero goals through advanced technology, consulting services, and an extensive network.


