- Article Summary
-
The construction industry—one of the world’s largest sources of carbon emissions and resource use—is undergoing a quiet revolution. As stakeholders from regulators to investors and communities demand a more sustainable, equitable, and accountable built environment, ESG (Environmental, Social, and Governance) principles are becoming embedded in every stage of the construction process. This article explores five critical ESG trends driving transformation in the global construction sector.
Green Materials and Carbon Reduction Strategies
Construction is responsible for an estimated 39% of global carbon emissions, with much of that embedded in materials like cement, steel, and glass. The push toward net-zero buildings has triggered a wave of innovation in low-carbon materials and construction techniques.
Key Developments:
- Adoption of low-carbon concrete and green steel.
- Bio-based materials such as cross-laminated timber (CLT) gaining traction.
- Prefabrication and modular construction for reduced waste and emissions.
Table: Emerging Green Materials in Construction (2024)
| Material | Carbon Savings (%) | Key Use Cases |
|---|---|---|
| Low-carbon concrete | 30–50% | Foundations, roadbeds |
| Green steel | 50–90% | Structural framing |
| Cross-laminated timber | 60–80% | Mid-rise buildings, schools |
| Recycled plastic bricks | 70–90% | Walls, landscaping, fencing |
These alternatives not only reduce emissions but also offer circularity, recyclability, and in many cases, lower life-cycle costs.
Resilience, Energy Efficiency, and Climate Adaptation
Buildings are not just sources of emissions—they are also vulnerable to the consequences of climate change. ESG-aligned construction increasingly integrates resilience and adaptation into design standards.
Focus Areas:
- Passive cooling and heating systems to reduce energy demand.
- Climate-adapted architecture, especially in coastal and wildfire-prone regions.
- Green roofs and permeable pavements to manage urban runoff and heat.
Chart: Energy Intensity of New Construction (kWh/m²/year)
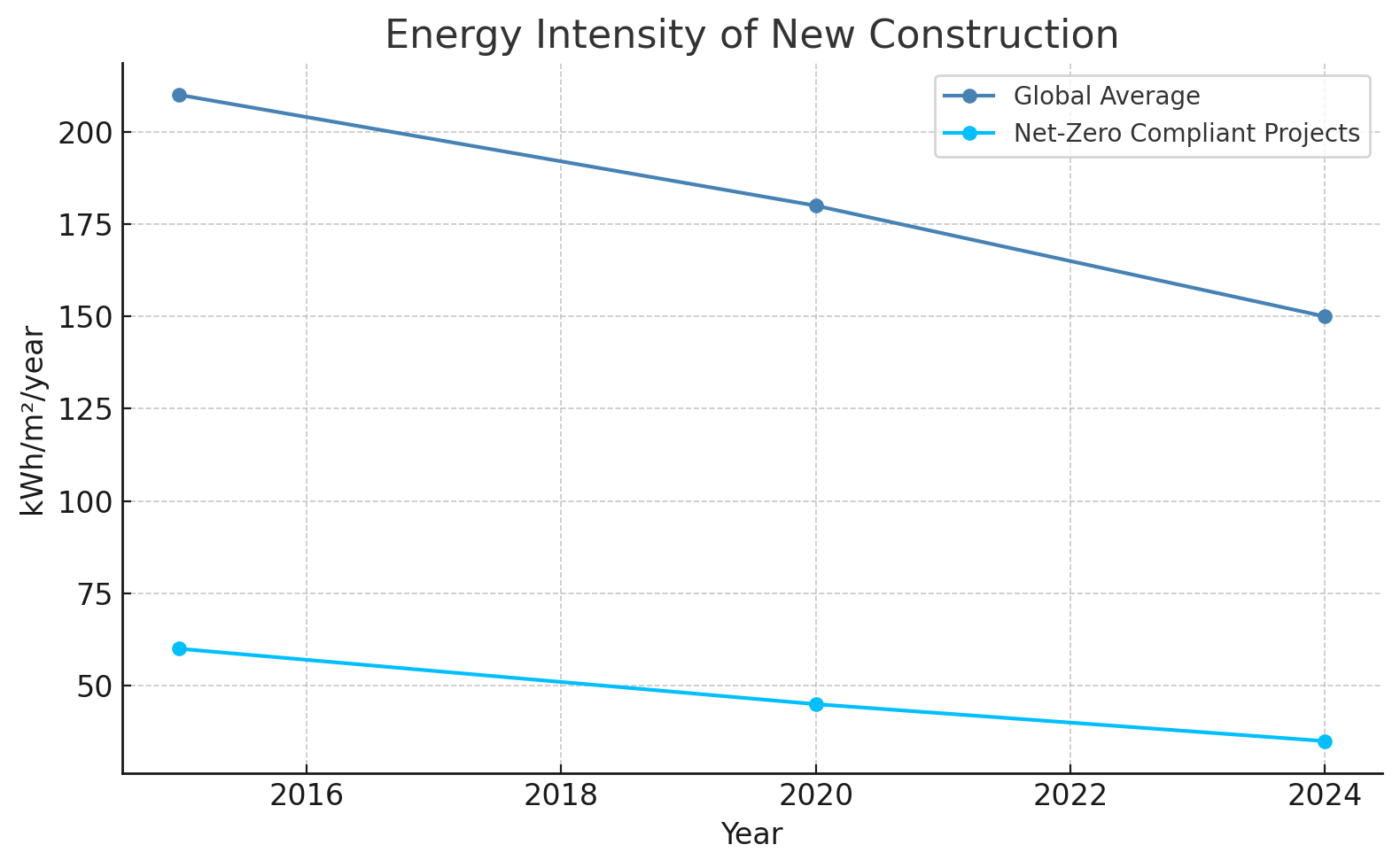
| Global Avg. | Net-Zero Compliant Projects
---------|-------------|------------------------------
2015 | 210 | 60
2020 | 180 | 45
2024 (E) | 150 | 35
Building codes in the EU, Canada, and parts of Asia now increasingly require climate risk assessments at the permitting stage, integrating resilience into compliance.
Workforce Safety, Equity, and Well-being
Construction remains one of the most hazardous professions globally. The ESG imperative has expanded the social agenda to encompass health, equity, and the psychological safety of workers and contractors.
Core Initiatives:
- Digital safety management systems and AI-powered hazard monitoring.
- DEI (Diversity, Equity, and Inclusion) programs at large construction firms.
- Fair wage certification and community-based hiring practices.
Table: Social Metrics in Construction (2024)
| Indicator | Global Average | ESG Leaders |
|---|---|---|
| Lost Time Injury Rate (LTIR) | 3.4 per 100 FTEs | < 1.2 per 100 FTEs |
| Female Representation | 13% | > 25% in ESG-focused firms |
| Mental Health Program Adoption | 42% | 100% in top-tier firms |
Social sustainability is now a requirement in public tenders across the EU and parts of the U.S., driving wider adoption across the industry.

Transparency, Certifications, and ESG Reporting
ESG reporting in construction has matured rapidly, driven by investor pressure, green finance requirements, and regulatory mandates. Certifications now play a vital role in signaling compliance and performance.
Popular Frameworks:
- LEED (Leadership in Energy and Environmental Design)
- BREEAM (Building Research Establishment Environmental Assessment Method)
- WELL Building Standard (focused on health and well-being)
- ISO 14001 for environmental management
Chart: Growth of Certified Green Buildings (Global, 2015–2024)
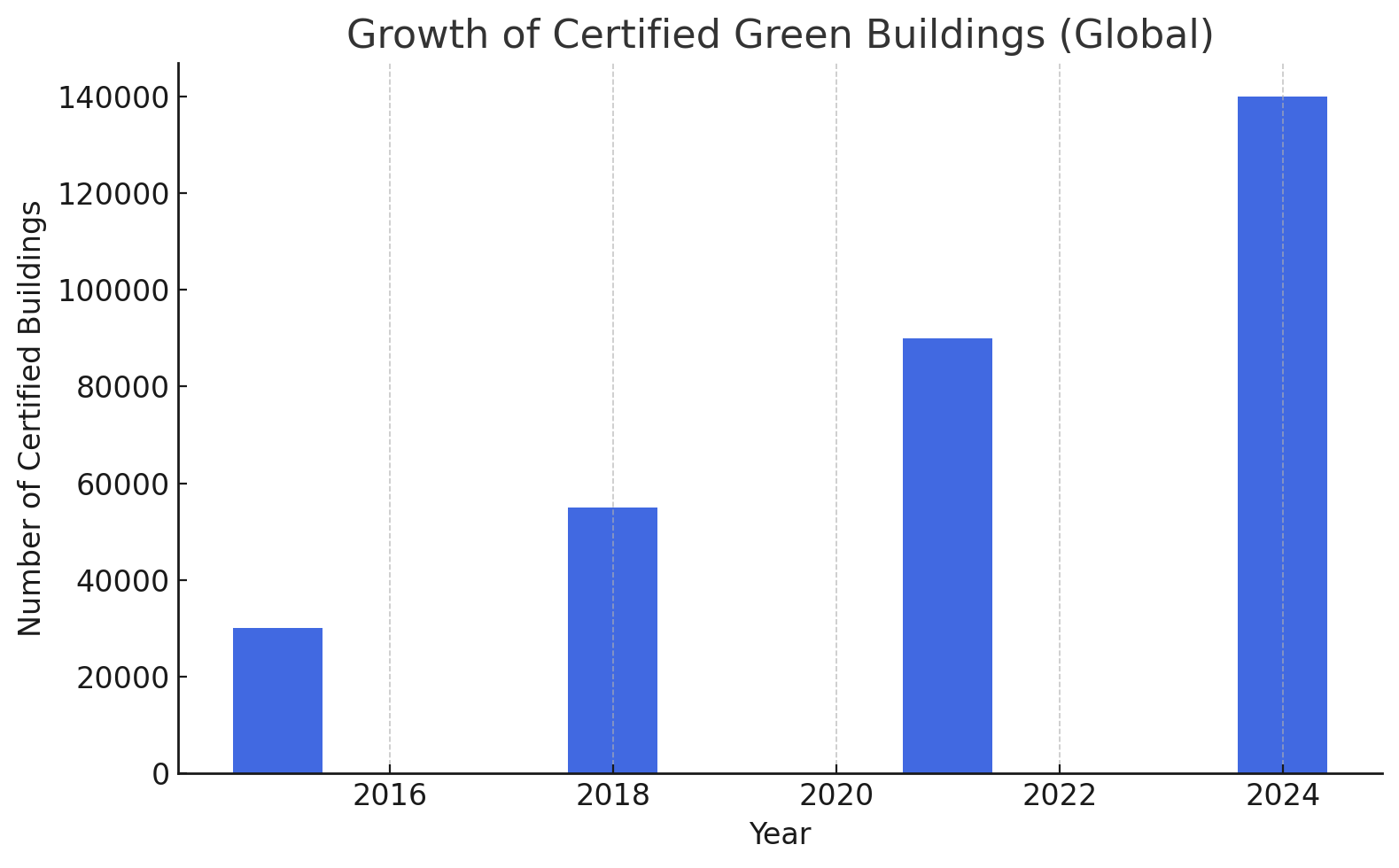
| Total Certified Buildings
---------|---------------------------
2015 | 30,000
2018 | 55,000
2021 | 90,000
2024 (E) | 140,000
Governments are also tying public infrastructure investment to ESG disclosures under policies like the EU Taxonomy and Sustainable Finance Disclosure Regulation (SFDR).
Digitalization and Smart Construction Practices
Digitalization is enabling more accurate ESG monitoring, efficient project execution, and lifecycle sustainability in the built environment.
Leading Tools:
- BIM (Building Information Modeling) for design and carbon forecasting.
- Drones and IoT for real-time site monitoring.
- Digital twins for energy and environmental simulation.
Table: Digital Adoption in Construction Firms (2024)
| Technology | Adoption Rate (%) | Primary ESG Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| BIM | 78% | Design optimization |
| IoT-based sensors | 54% | Waste, emissions tracking |
| Carbon forecasting tools | 47% | Scope 3 emission calculations |
| Lifecycle assessment (LCA) software | 61% | End-to-end sustainability |
Firms that can provide transparent, data-backed ESG metrics gain competitive advantage in securing contracts and financing.
Conclusion: From Green Buildings to Green Business
The construction industry is evolving from ESG as a compliance task to ESG as a strategic growth driver. Whether through carbon-negative materials, inclusive hiring, or digital ESG traceability, leading firms are reimagining what it means to build sustainably.
As governments tighten reporting rules and investors demand more, the pressure to embed ESG at the blueprint level will only grow. The future of construction is not only about building structures—it’s about building trust, resilience, and long-term value.
Why Work with ASUENE Inc.?

ASUENE USA Inc., a subsidiary of Asuene Inc., is a key player in carbon accounting, offering a comprehensive platform that measures, reduces, and reports emissions, including Scope 1-3, with expertise in decarbonization. Asuene serves over 10,000 clients worldwide, providing an all-in-one solution that integrates GHG accounting, ESG supply chain management, a Carbon Credit exchange platform, and third-party verification.
ASUENE supports companies in achieving net-zero goals through advanced technology, consulting services, and an extensive network.

