- Article Summary
-
From Venice to Kyoto, the surge in global travel has brought significant economic benefits—but also rising environmental, cultural, and social pressures. This phenomenon, known as overtourism, refers to the excessive influx of tourists to destinations beyond their carrying capacity, often leading to resource strain, resident displacement, and ecosystem degradation.
With travel rebounding in a post-COVID world and tourism emissions projected to grow 25% by 2030, managing overtourism has become a pressing issue for cities, tourism boards, and ESG-minded businesses. This article explores the systemic risks of overtourism and presents ESG-aligned solutions across policy, data analytics, infrastructure, and stakeholder engagement.
Understanding the Impacts of Overtourism
Overtourism affects local communities and ecosystems in several interconnected ways:
- Environmental: Increased waste, water usage, carbon emissions, and habitat disruption.
- Social: Rising housing prices, noise pollution, and cultural commodification.
- Economic: Overreliance on seasonal income, vulnerability to external shocks, infrastructure overuse.
Table: Overtourism Hotspots and Key Pressures
| Destination | Main Challenge | Response in Place |
|---|---|---|
| Venice, Italy | Cruise ship congestion | Tourist caps, port relocation plan |
| Kyoto, Japan | Heritage site overuse | Tourist education, guided pathways |
| Barcelona, Spain | Resident pushback and housing cost | Tourism tax, license restrictions |
| Bali, Indonesia | Environmental degradation | Entry fee, conservation programs |
ESG Strategies for Managing Tourism Sustainability
Environmental (E)
- Carbon impact disclosure: Tourism operators begin reporting emissions (Scope 3 focus).
- Sustainable mobility: Electrified shuttles, bike paths, pedestrian zones.
- Waste systems: Composting, reusable foodware mandates in high-volume areas.
Social (S)
- Community engagement: Involving residents in tourism planning decisions.
- Capacity limits: Dynamic ticketing or daily visitor quotas.
- Local benefit assurance: Supporting small, locally-owned enterprises and artisans.
Governance (G)
- Destination stewardship councils: Public-private governance models.
- Data transparency: Real-time visitor monitoring systems (e.g., apps, sensors).
- Policy integration: Tourism embedded in urban, climate, and transport planning.

Data-Driven Management: Monitoring and Prevention
Smart tourism strategies rely on data to forecast and manage visitor flows:
- Geo-tracking apps inform tourists of real-time crowding.
- Digital passes and QR codes enable usage tracking at heritage sites.
- AI-based models simulate capacity thresholds and optimize entry timing.
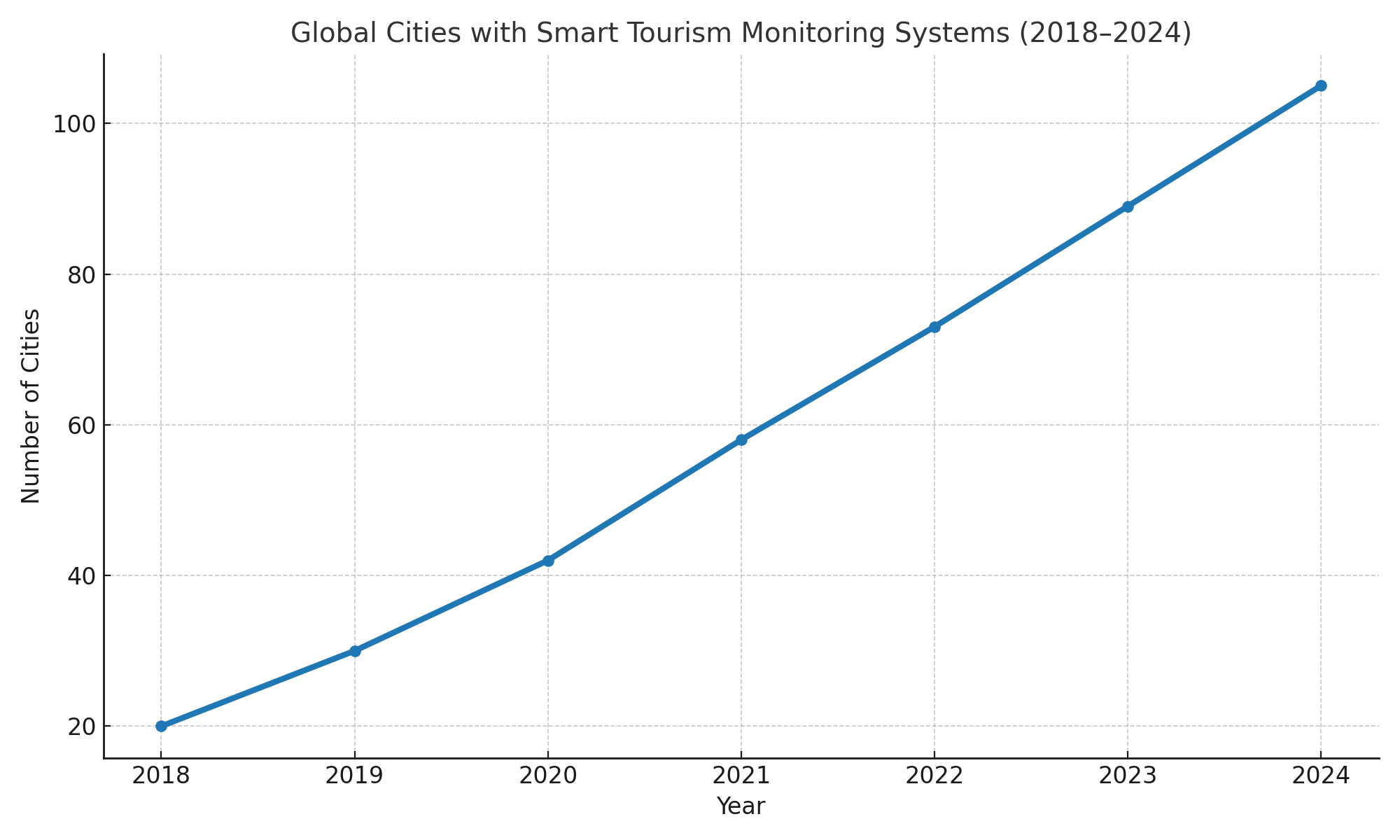
Many cities, like Amsterdam and Dubrovnik, are piloting predictive dashboards that combine foot traffic sensors with weather, transport, and event data to better allocate resources and inform tourists.
Graph: Global Cities with Smart Tourism Monitoring Systems (2018–2024)
Stakeholder Collaboration: Multi-Level ESG Governance
No single entity can manage overtourism alone. Effective responses involve:
- Municipalities: Enforcing zoning, permits, and environmental standards.
- Businesses: Adopting visitor impact assessments, sustainability certifications (e.g., GSTC).
- Investors: Evaluating tourism-linked assets through an ESG lens.
- Citizens: Participatory platforms to share concerns and co-design solutions.
Innovative financing models like “green tourism bonds” are emerging to fund regenerative infrastructure (e.g., renewable-powered transit, nature restoration zones).
Conclusion
Overtourism is a climate, equity, and governance issue wrapped in one. Addressing it requires more than temporary caps—it demands systemic ESG integration, from data-driven planning and infrastructure design to inclusive policy and community empowerment.
By aligning tourism management with ESG principles, destinations can preserve their cultural and natural capital, improve resident wellbeing, and ensure long-term economic resilience in a rapidly changing world
Why Work with ASUENE Inc.?
Asuene is a key player in carbon accounting, offering a comprehensive platform that measures, reduces, and reports emissions, including Scope 1-3, with expertise in decarbonization. Asuene serves over 10,000 clients worldwide, providing an all-in-one solution that integrates GHG accounting, ESG supply chain management, a Carbon Credit exchange platform, and third-party verification.
ASUENE supports companies in achieving net-zero goals through advanced technology, consulting services, and an extensive network.


