- Article Summary
-
Life Cycle Assessment (LCA) is rapidly evolving from a compliance-driven reporting tool to a strategic driver of sustainable innovation. As environmental regulations tighten and investor expectations grow, companies are leveraging LCA not only to identify environmental “hotspots,” but to guide upstream product development, supplier engagement, and net-zero transformation. This article explores the global best practices and standards shaping modern LCA, the strategic use cases across industries, and how digital platforms like Asuene LCA are transforming complex assessments into real-time, actionable insights for executives committed to sustainable growth.
The Evolution of LCA: From Compliance to Strategy
Historically, LCA was primarily used to meet environmental disclosure requirements or support eco-labeling programs. Today, its role has shifted dramatically. LCA is now a critical component of sustainability strategy for forward-looking firms across sectors — from electronics and automotive to apparel and consumer goods.
What’s driving this shift?
- Climate targets: Science-Based Targets initiative (SBTi) commitments require companies to track emissions across Scopes 1, 2, and 3 — much of which LCA helps quantify.
- Investor scrutiny: ESG ratings increasingly reward companies that disclose product-level environmental impact data.
- Consumer demand: Transparency about product footprints influences brand loyalty and purchasing decisions.
- Regulatory change: The EU’s Digital Product Passport and Ecodesign for Sustainable Products Regulation will soon require detailed lifecycle data disclosure across value chains.
As a result, leading companies now treat LCA as a strategic compass, not just an environmental report card.
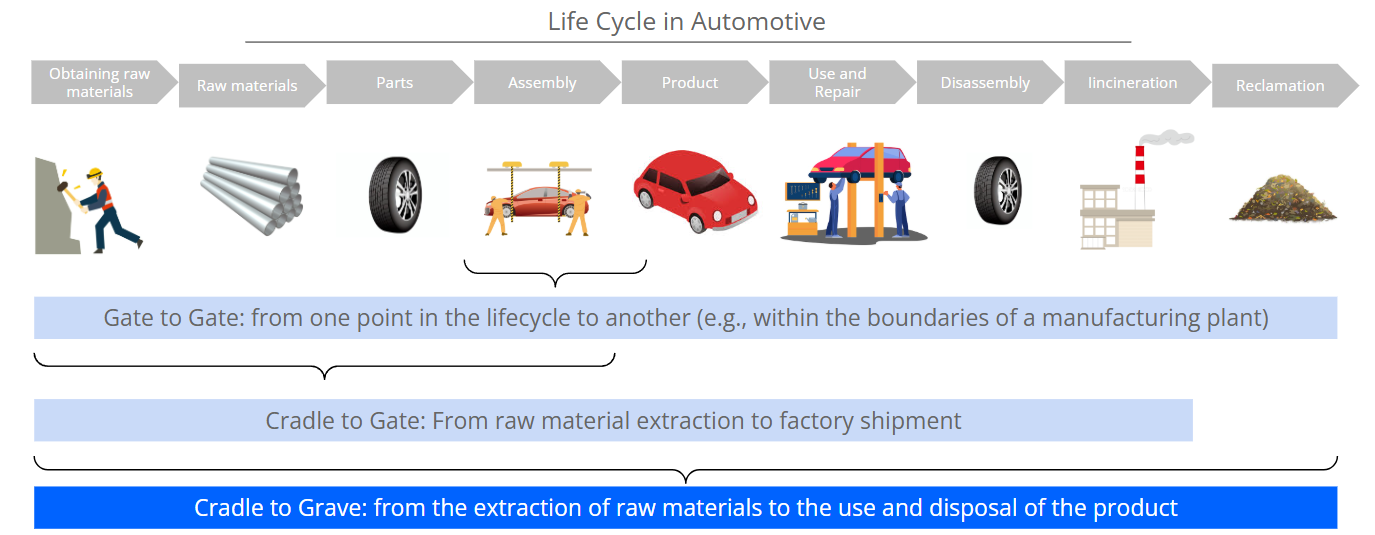
ISO 14040/14044: Global Frameworks for Rigorous Assessment
At the heart of credible LCA lies the ISO 14040 and ISO 14044 standards, which define four key phases:
- Goal and scope definition
- Inventory analysis (LCI)
- Impact assessment (LCIA)
- Interpretation
These stages ensure consistency, transparency, and comparability in LCA studies. However, they also require robust data from multiple life stages — raw material extraction, manufacturing, transport, use, and end-of-life.
Many organizations struggle with:
- Disparate data sources across the supply chain
- Complex modeling of multi-tier supplier emissions
- Keeping inventories updated with fast-changing product lines
This is where digital LCA platforms, embedded with global emission databases and AI-powered estimation engines, play an increasingly pivotal role.
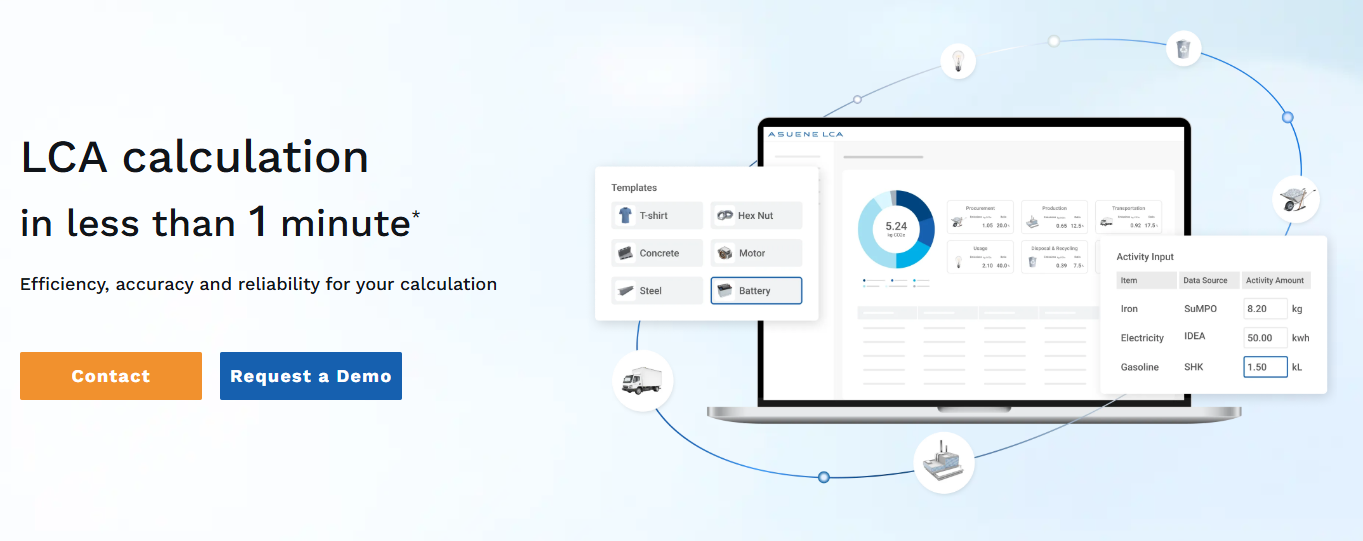
Strategic Use Cases of LCA in Business
Product Design and Eco-Innovation
By modeling the environmental impact of products at the concept stage, companies can:
- Select lower-impact materials (e.g., recycled aluminum vs. virgin steel)
- Identify energy-intensive manufacturing processes
- Optimize packaging to reduce transportation emissions
Example: A global consumer electronics firm used LCA to redesign its packaging, cutting GHG emissions by 24% and reducing air freight costs by 12%.
Supply Chain Decarbonization
LCA provides a quantitative lens on Scope 3 emissions embedded in purchased goods and services. It enables procurement teams to:
- Benchmark suppliers by carbon intensity
- Prioritize low-impact materials
- Engage in supplier capacity-building for data transparency
Example: A fashion retailer conducted LCAs across its textile categories and shifted procurement toward organically grown, low-water-use cotton, reducing upstream emissions by 30%.
Net-Zero Strategy Alignment
LCA helps connect product-level emissions to enterprise-wide climate goals. It enables:
- Setting product-level carbon reduction targets
- Integrating LCA metrics into ESG reporting
- Monitoring progress toward net-zero at the SKU level
This bottom-up approach increases credibility in ESG disclosure and aligns internal functions — from R&D to sales — with decarbonization objectives.

Digital Transformation of LCA: Overcoming the Data Bottleneck
Traditional LCAs, conducted by consultants using spreadsheet-based models, are time-consuming and resource-intensive. Today’s business landscape demands:
- Scalability across hundreds or thousands of SKUs
- Real-time data updates from ERP or supply chain systems
- Transparency for both internal users and external stakeholders
Modern LCA platforms address these needs by offering:
- Cloud-based architecture for collaborative access
- Pre-integrated emission databases (e.g., ecoinvent, Gabi)
- Automated impact calculation engines using AI
- Dashboard visualization tools for executive insights
These tools not only reduce the burden on sustainability teams but empower cross-functional decision-making.
Metrics that Matter: Turning LCA Results into Action
For LCA to become a strategic tool, its findings must be interpretable and actionable. Key metrics often visualized include:
| Metric | Purpose |
|---|---|
| Carbon Footprint (CO₂e) | Quantifies global warming potential per product |
| Water Footprint | Evaluates freshwater usage across lifecycle |
| Resource Depletion Index | Measures use of non-renewable materials |
| Human Health Impact | Assesses toxicity and respiratory effects |
| Recyclability Score | Estimates end-of-life recovery potential |
These indicators feed directly into:
- Eco-design decisions
- Sustainable procurement criteria
- ESG reporting under CSRD, CDP, or TCFD
Real-World Impact: Case Studies Across Sectors
Consumer Goods
A global food and beverage company used LCA to compare traditional and plant-based product lines. The analysis revealed 62% lower CO₂e emissions in the plant-based line, guiding a product portfolio shift.
Automotive
An EV manufacturer conducted cradle-to-grave LCAs of its vehicle models. By switching to recycled aluminum and sourcing renewable electricity, it reduced lifecycle GHG emissions per vehicle by 35%.
Electronics
An ICT firm implemented LCA across its full product range using a digital platform, achieving 80% faster reporting and identifying $5M in potential cost savings from material redesign.
The Road Ahead: Scaling LCA for Sustainability Leadership
As LCA moves into the digital era, it holds the potential to:
- Serve as a core KPI in board-level ESG dashboards
- Drive climate-positive product innovation
- Facilitate transparent communication with regulators and investors
However, to reach this potential, companies need tools that remove friction from the process — particularly in data gathering, modeling, and decision-making integration.
Introducing Asuene LCA: Your Digital Engine for Lifecycle Intelligence
To support companies on this journey, Asuene has developed Asuene LCA — a next-generation lifecycle assessment platform that empowers sustainability teams and executives with:
- AI-powered impact modeling across materials, manufacturing, logistics, use, and end-of-life
- Seamless integration with upstream supplier data and internal ERP systems
- Global emission database support for ISO 14040/14044-compliant analysis
- Intuitive dashboards for communicating LCA results to stakeholders
- Scenario simulation tools to evaluate decarbonization strategies
Whether you are designing lower-impact products, responding to CSRD or SEC disclosure mandates, or aiming to meet your net-zero targets, Asuene LCA transforms lifecycle complexity into strategic clarity.
Let LCA be your compass. And let Asuene be your guide.
Why Work with ASUENE Inc.?

ASUENE USA Inc., a subsidiary of Asuene Inc., is a key player in carbon accounting, offering a comprehensive platform that measures, reduces, and reports emissions, including Scope 1-3, with expertise in decarbonization. Asuene serves over 10,000 clients worldwide, providing an all-in-one solution that integrates GHG accounting, ESG supply chain management, a Carbon Credit exchange platform, and third-party verification.
ASUENE supports companies in achieving net-zero goals through advanced technology, consulting services, and an extensive network.
Download Our Expert Publications!

