- Article Summary
-
Introduction
The sustainable finance market has witnessed explosive growth over the past decade, with green, social, and sustainability-linked bonds (GSS+ bonds) becoming mainstream instruments for companies and governments seeking to finance their environmental and social initiatives. However, this growth has been accompanied by increasing scrutiny over greenwashing, credibility gaps, and inconsistent disclosure standards. In response, Institutional Shareholder Services (ISS), a leading proxy advisory and ESG analytics firm, has launched its Sustainability Bond Ratings—a new methodology designed to enhance transparency, comparability, and investor trust in the ESG debt space.
This article examines the structure and significance of ISS’s new ratings, compares it with other notable frameworks, and discusses the broader implications for issuers, investors, and ESG reporting.
ISS – A Trusted ESG Authority
Founded in 1985, Institutional Shareholder Services (ISS) has become a globally recognized authority in proxy advisory, corporate governance, ESG ratings, and sustainable finance analytics. With over 4,000 institutional clients—including pension funds, asset managers, and insurance companies—ISS plays a pivotal role in shaping investment decisions and corporate behavior.
Through its subsidiary ISS ESG, the firm offers an extensive range of products, including:
- Corporate ESG Ratings
- Carbon Risk Ratings
- Sustainable Finance Assessments
- Screening Solutions aligned with international norms (e.g., UN Global Compact, OECD Guidelines)
The new Sustainability Bond Ratings represent a strategic expansion of ISS ESG’s toolkit into the increasingly complex world of sustainable finance instruments.

Overview of ISS Sustainability Bond Ratings
Scope and Coverage
The ISS Sustainability Bond Ratings provide independent evaluations of two major types of ESG-related bonds:
- Use-of-Proceeds Bonds (Green, Social, and Sustainability Bonds)
- Sustainability-Linked Bonds (SLBs)
Each bond is assessed along two distinct dimensions:
- Framework Rating: Evaluates the structural alignment of the bond issuance with established sustainability principles (e.g., ICMA’s Green Bond Principles).
- Issuer Profile Score: Measures the issuer’s ESG performance and ability to deliver on intended impact.
Rating Scale and Methodology
ISS employs a five-point scale for its Framework and Issuer scores:
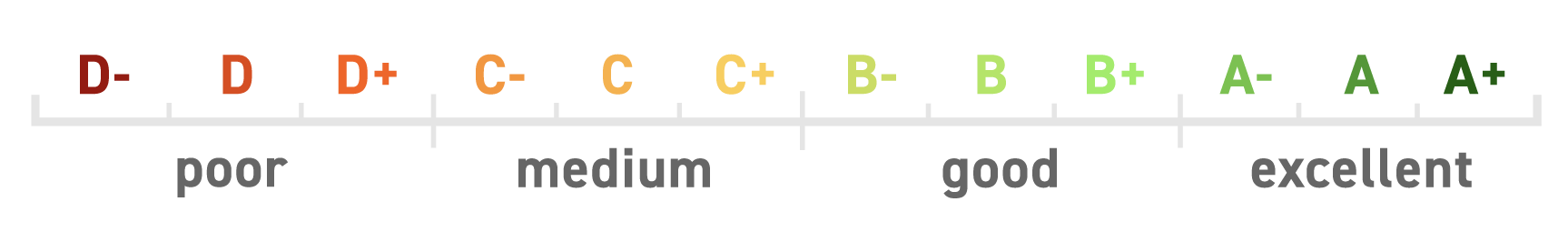
- Excellent
- Good
- Moderate
- Weak
- Poor
These ratings are derived using over 50 indicators, combining qualitative assessments and quantitative data. The framework considers factors such as:
| Evaluation Focus | Sample Indicators |
|---|---|
| Use-of-Proceeds Bonds | Project eligibility, reporting quality, impact metrics |
| Sustainability-Linked | KPI relevance, SPT ambition, fallback mechanisms |
| Issuer Performance | ESG ratings, controversy screening, carbon trajectory |
Importantly, ISS integrates forward-looking perspectives, assessing not just current performance but the likelihood of sustained or improving impact over time.
Differentiators from Other Frameworks
While ISS is not the first to assess sustainable bonds, its approach introduces several key differentiators:
Comparison with Second Party Opinion Providers (SPOs)
| Criteria | ISS Sustainability Bond Ratings | SPO Providers (e.g. Sustainalytics, Moody’s,) |
|---|---|---|
| Scoring System | Dual rating (Framework + Issuer) | Generally qualitative or binary |
| Forward-Looking Input | Integrated | Limited or absent |
| Issuer Evaluation | Included | Typically excluded or minimal |
| Public Accessibility | Scaled products, with ratings index | Often confidential unless disclosed by issuer |
| Quantitative Integration | 50+ indicators, ESG data-based | Often narrative-based |
Unlike most SPOs that focus primarily on the framework quality, ISS goes further by explicitly assessing the issuer’s ESG track record and strategic alignment with sustainable goals.
Comparison with ESG Credit Ratings
Credit rating agencies like S&P and Moody’s have begun integrating ESG into credit assessments. However, their focus remains credit risk, not sustainability impact. ISS offers a dedicated impact-oriented lens that complements, rather than duplicates, credit risk assessments.

Implications for Issuers and Investors
For Issuers: Strategic Planning and Market Positioning
For corporate issuers, ISS’s new ratings provide several strategic benefits:
- Benchmarking tool for structuring credible bonds
- Pre-issuance feedback to refine KPIs and SPTs
- Enhanced market reputation and investor confidence
- Better alignment with EU Green Bond Standard and upcoming ISSB and SEC disclosure regimes
Issuers with strong ESG practices and transparent frameworks may see improved demand and pricing for their bonds. Conversely, low ratings may act as a warning signal, prompting governance or strategy reforms.
For Investors: Due Diligence and Portfolio Risk Management
From an investor’s perspective, the ISS ratings help:
- Distinguish between substantive and symbolic sustainability claims
- Support impact-focused investment mandates (e.g., Article 9 SFDR funds)
- Evaluate transition risk in bond portfolios
- Align holdings with frameworks such as EU Taxonomy, TCFD, or NGFS guidelines
Regulatory Context and Future Outlook
As the regulatory environment around sustainable finance tightens, ISS’s comprehensive approach may set a new standard in the industry.
Alignment with Global Standards
ISS’s framework is designed to align with or complement:
- ICMA’s Green and Social Bond Principles
- EU Green Bond Standard (EU GBS)
- Climate Bonds Initiative (CBI) criteria
- ISSB and EFRAG standards on climate and ESG disclosures
Such alignment positions ISS as a key enabler of regulatory compliance and cross-border comparability.
Market Influence and Future Expansion
With institutional investors under increasing pressure to demonstrate ESG integration, ISS’s Sustainability Bond Ratings may become an essential part of due diligence processes, particularly for sovereign bonds, emerging market issuers, and complex SLBs.
Furthermore, ISS could expand the methodology to:
- Covered bonds and ABS products
- Transition bonds
- Municipal or sub-sovereign debt
Conclusion
By introducing the Sustainability Bond Ratings, ISS is not merely adding another product to its ESG portfolio—it is setting a new benchmark for accountability, comparability, and credibility in the sustainable finance landscape. As investors grow more discerning and regulators tighten their oversight, tools like this will be essential in ensuring that capital flows are truly aligned with environmental and social progress.
In a market often clouded by ambiguity and marketing-driven claims, ISS offers clarity. The future of ESG investing may very well depend on such credible third-party assessments that can bridge the gap between intention and impact.
Why Work with ASUENE Inc.?

ASUENE USA Inc., a subsidiary of Asuene Inc., is a key player in carbon accounting, offering a comprehensive platform that measures, reduces, and reports emissions, including Scope 1-3, with expertise in decarbonization. Asuene serves over 10,000 clients worldwide, providing an all-in-one solution that integrates GHG accounting, ESG supply chain management, a Carbon Credit exchange platform, and third-party verification.
ASUENE supports companies in achieving net-zero goals through advanced technology, consulting services, and an extensive network.

