- Article Summary
-
Introduction
In an era where environmental, social, and governance (ESG) factors are becoming central to investor decision-making, ISS ESG — the responsible investment arm of Institutional Shareholder Services Inc. — plays a crucial role in shaping market behavior. Its ESG rating system has become one of the most widely used benchmarks for assessing corporate sustainability, influencing trillions of dollars in global capital. Investors, asset managers, and corporations turn to ISS not just for proxy advisory services, but increasingly for its insights into ESG risks and opportunities.
ISS ESG ratings are designed to evaluate how well companies integrate ESG risks into their corporate strategy and operations. However, unlike credit ratings, which are grounded in relatively uniform financial data, ESG ratings often rely on heterogeneous, sometimes non-standardized information. As such, understanding how ISS determines its scores, what those scores signify, and how they compare with other frameworks is essential for stakeholders striving to lead in sustainable finance.

This article explores the structure and methodology of the ISS ESG rating, compares it with competing frameworks, examines its influence on corporate and investor behavior, and analyzes emerging challenges and trends. Data visualizations will support a comprehensive examination, offering a clear lens through which to understand ISS’s growing footprint in ESG investing.
The Methodology Behind ISS ESG Ratings
ISS ESG applies a dual-layered assessment methodology built around sector-specific materiality. Ratings are awarded based on a company’s exposure to ESG risks and the effectiveness of its management of these issues. The primary output is a letter grade ranging from D- to A+, where a company must achieve at least a “C” (the sector-specific threshold) to be classified as “Prime”.
Scoring Frequency and Update Cycle
ISS ESG Corporate Ratings are updated annually, although interim updates are possible when material new information arises — for example, a significant environmental incident, governance scandal, or major change in policy. In the 2024 update, ISS also aligned update frequency with public disclosure cycles to ensure timely incorporation of sustainability reports, regulatory filings, and verified third-party data.
Latest Enhancements in 2024
Key improvements this year included:
- The Governance QualityScore (GQS) expanded to cover 12 new indicators, including cybersecurity policy strength, board climate competency, and shareholder rights in virtual meetings.
- Environmental & Social QualityScores (E&S QS) were broadened to assess over 340 metrics across 20+ sectors, with materiality maps now incorporating the latest SASB-aligned topics.
- A new “Double Materiality Lens” was introduced, accounting for both financial impact and societal/environmental externalities — reflecting emerging EU standards under CSRD.
Chart 1: ISS ESG Rating Structure and Key Inputs (2024)
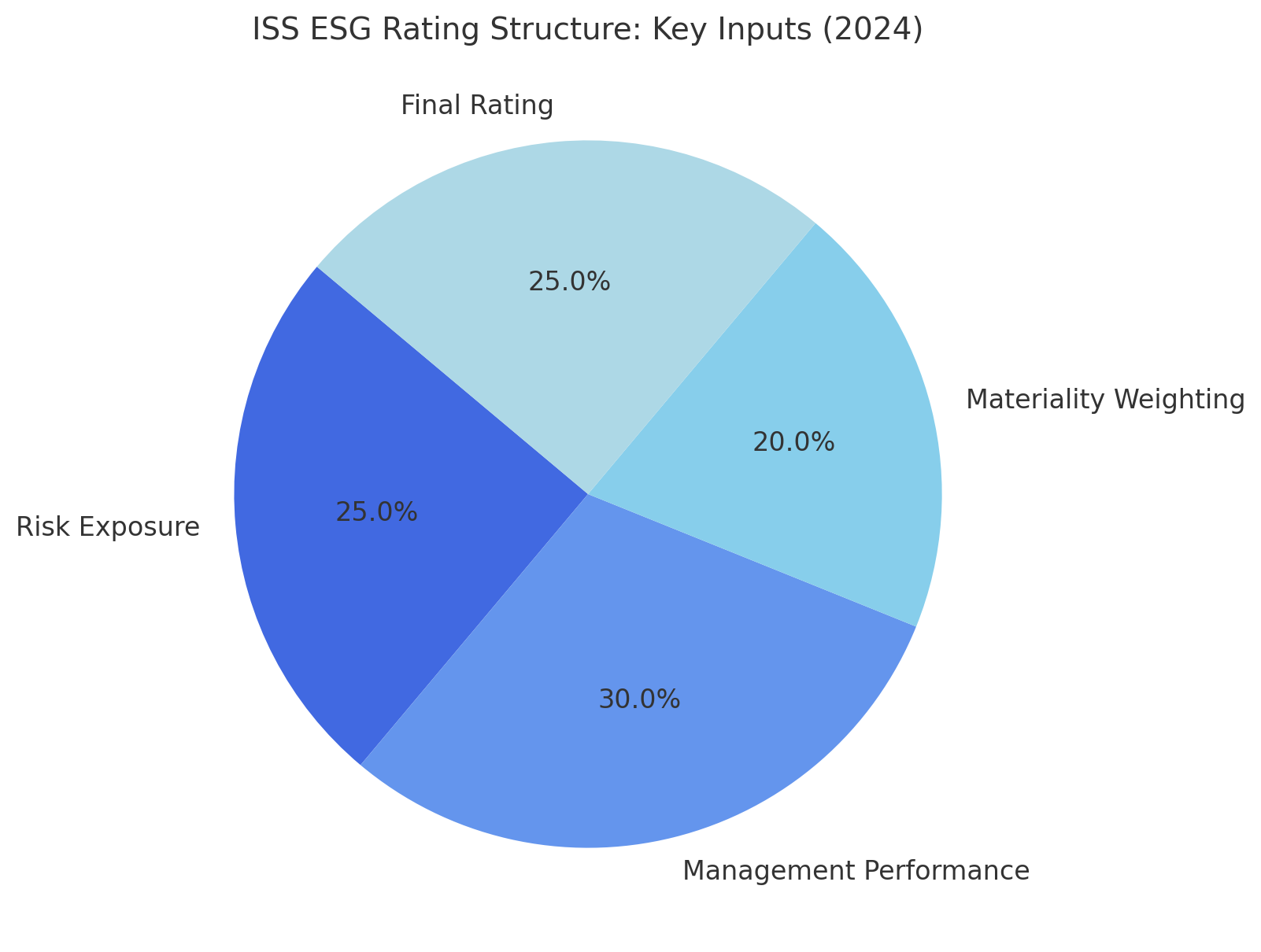
How Companies Can Achieve and Maintain Prime Status
For companies aiming to earn or retain Prime status — a designation highly favored by ESG-conscious investors — a clear, proactive ESG strategy is essential. The following actions are commonly undertaken by leading companies to align with ISS ESG criteria:
1. ESG Governance Integration
- Establish a dedicated ESG oversight body (e.g., board committee or cross-functional working group).
- Ensure ESG-linked compensation for executives tied to measurable performance indicators.
2. Materiality-Based Target Setting
- Conduct double materiality assessments using stakeholder engagement and industry benchmarks.
- Disclose science-based targets for emissions reductions and track progress transparently.
3. Transparency and Disclosure
- Align reporting with GRI, SASB, and TCFD standards.
- Publish audited ESG data and participate in third-party ESG verification (e.g., CDP, SBTi).
4. Risk Management and Policy Strengthening
- Address supply chain due diligence, particularly for human rights and carbon intensity.
- Implement robust whistleblower, anti-bribery, and cyber-resilience programs.
5. Continuous Monitoring and Engagement
- Monitor ISS ESG interim updates and peer developments.
- Maintain open channels with ESG rating agencies and prepare management responses to rating inquiries.
Typical Gaps Identified in ISS ESG Rating Reviews (2023–2024)
| Gap Category | Common Issues Identified | Recommended Response |
|---|---|---|
| Governance | No climate oversight at board level | Establish ESG board committee |
| Social | Weak supply chain human rights audit | Conduct third-party social audits |
| Environment | Lack of Scope 3 emissions reporting | Develop supply chain data systems |
| Disclosure | ESG KPIs not independently assured | Obtain external assurance |
Comparative Analysis: ISS ESG vs. Other ESG Rating Agencies
While ISS ESG offers a robust framework for evaluating ESG performance, it’s essential to understand how it compares to other prominent ESG rating agencies like MSCI and Sustainalytics.
Comparative Overview of ESG Rating Agencies
| Feature | ISS ESG | MSCI ESG Ratings | Sustainalytics ESG Risk Ratings |
|---|---|---|---|
| Rating Scale | D- to A+ | CCC to AAA | Negligible to Severe Risk |
| Methodology Focus | Absolute performance, sector-specific thresholds | Relative performance, industry-adjusted | Risk exposure and management |
| Update Frequency | Annual + ad hoc updates | Quarterly | Monthly |
| “Leader” Designation | Prime (C or higher) | Leader (AA/AAA) | Low ESG Risk (<10) |
| Global Coverage | >10,000 issuers, expanding in Asia | >8,500 issuers | >13,000 issuers |
ISS’s absolute “Prime” rating contrasts with MSCI’s relative industry ranking and Sustainalytics’ risk-based scale. Each serves distinct investor needs, but ISS’s sectoral depth and increasing transparency make it particularly effective for engagement-focused and impact-driven strategies.

Real-World Impact and Investor Behavior
ISS ESG scores directly impact investment decisions, engagement intensity, and cost of capital. Several major asset managers (including BlackRock and Amundi) now integrate ISS ESG ratings into screening, stewardship, and thematic funds.
Chart 2: Impact of Prime Rating on Investor Flows (2022–2024)
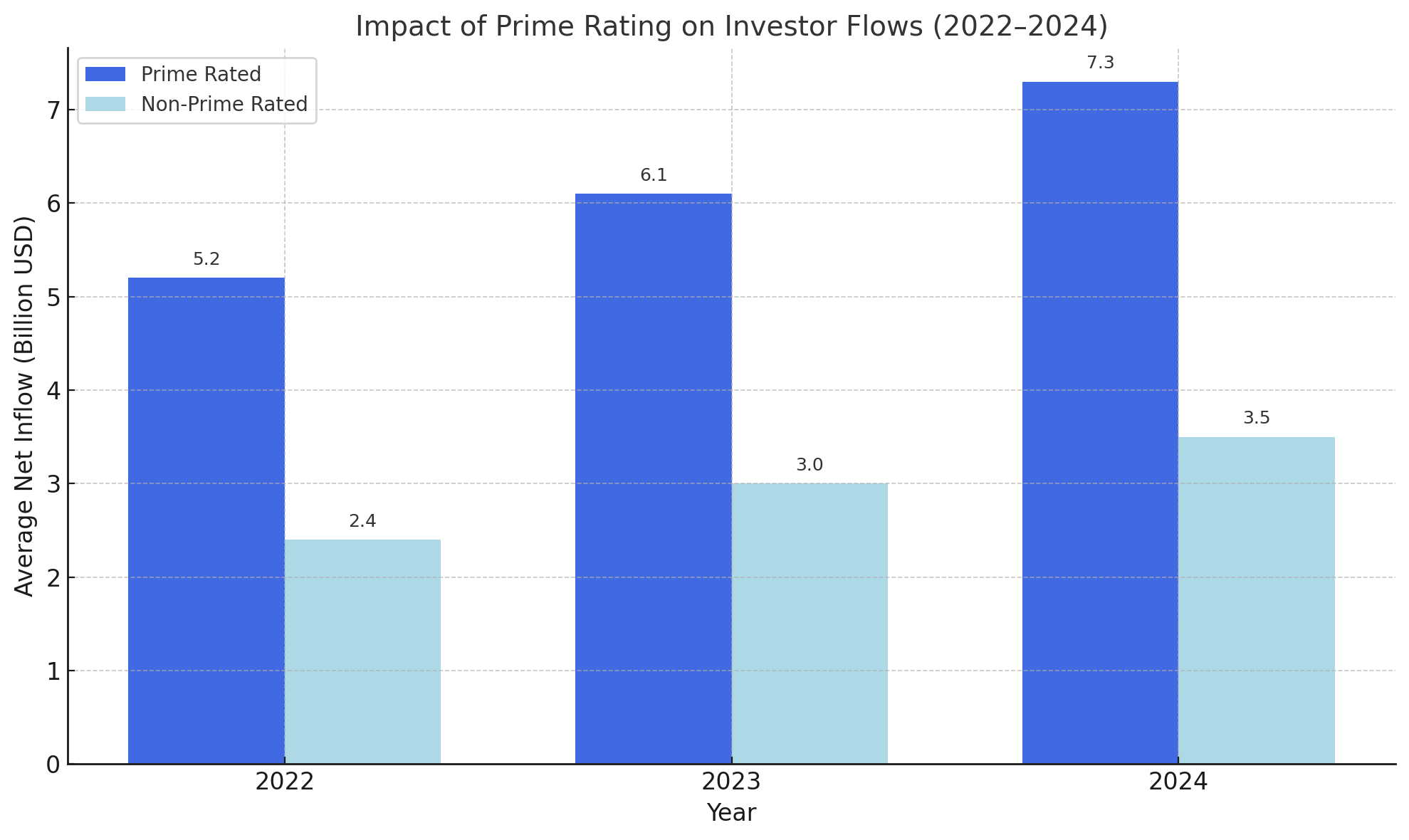
Moreover, companies receiving a downgrade in ISS ESG scores often experience shareholder pressure, engagement letters, and in some cases, proxy voting consequences during annual general meetings.
Meanwhile, ISS ESG’s engagement arm helps investors facilitate dialogue with underperformers, offering engagement plans and milestone tracking, making it a collaborative — not just punitive — tool.
Challenges and Future Outlook
Despite methodological rigor, ESG ratings, including ISS ESG, face criticisms related to opacity, subjectivity, and inconsistency across agencies. To address this:
- ISS ESG has committed to greater transparency, publishing methodology guides and sector-specific FAQs.
- Anticipated alignment with CSRD and SEC climate rules will further standardize inputs and disclosure timelines.
Technological integration is another area of focus. ISS is exploring machine learning models to detect controversies in real time and using satellite data for environmental verification.
Future Priorities for ESG Rating Agencies (Survey of Asset Managers, 2024)
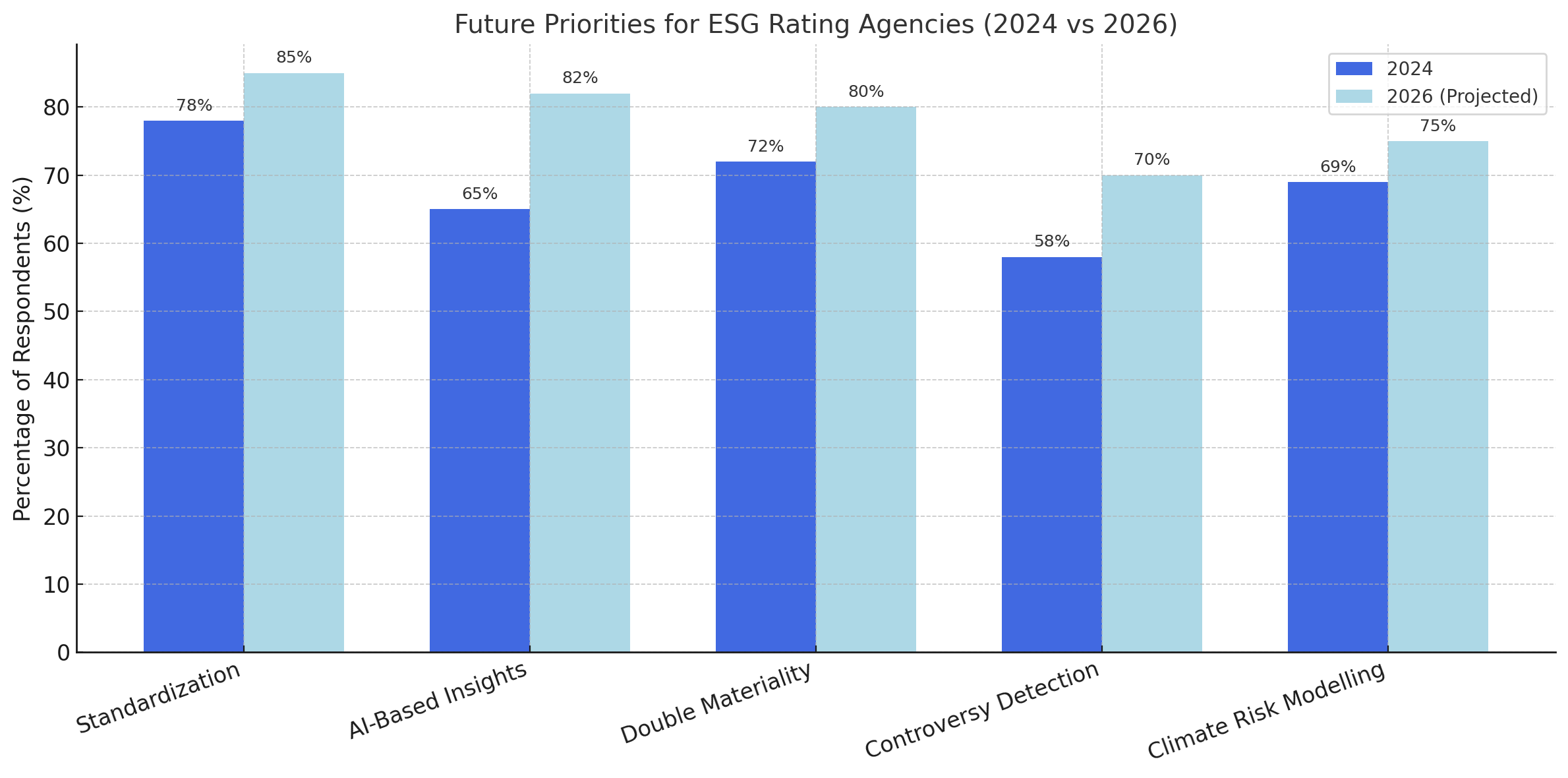
As regulation tightens and investor expectations rise, the future of ESG ratings — and ISS ESG in particular — hinges on their ability to adapt, verify, and influence outcomes, not merely measure them.
Conclusion
ISS ESG ratings are no longer just a tool for investors—they are a roadmap for corporate sustainability strategy. With annual scoring cycles, robust updates, and the coveted “Prime” designation, ISS ESG provides a clear framework for companies aiming to lead on ESG.
By aligning governance, risk management, and disclosure with ISS standards, companies can not only improve their ratings but also build long-term stakeholder trust. As ESG integration deepens across markets, ISS ESG’s role will continue to evolve — from rater to enabler, from benchmark to blueprint for a sustainable global economy.
Why Work with ASUENE Inc.?
Asuene is a key player in carbon accounting, offering a comprehensive platform that measures, reduces, and reports emissions, including Scope 1-3, with expertise in decarbonization. Asuene serves over 10,000 clients worldwide, providing an all-in-one solution that integrates GHG accounting, ESG supply chain management, a Carbon Credit exchange platform, and third-party verification.
ASUENE supports companies in achieving net-zero goals through advanced technology, consulting services, and an extensive network.



