- Article Summary
-
As digital infrastructure becomes the nervous system of the modern world, the information technology (IT) industry is under growing scrutiny for its environmental and social impact. From data center emissions to supply chain ethics, ESG (Environmental, Social, and Governance) considerations are no longer peripheral—they’re strategic imperatives. This article explores five major ESG trends reshaping the IT sector in 2024 and beyond.
Green Data Centers and the Energy Dilemma
IT infrastructure, particularly data centers, consumes enormous amounts of electricity. With global digital traffic and AI workloads soaring, energy efficiency is now a top environmental priority.
Key Responses:
- Shift to liquid cooling and renewable-powered data centers.
- Investment in low-PUE (Power Usage Effectiveness) facilities.
- AI-optimized server utilization and workload distribution.
Chart: Average PUE of Data Centers by Region (2024)
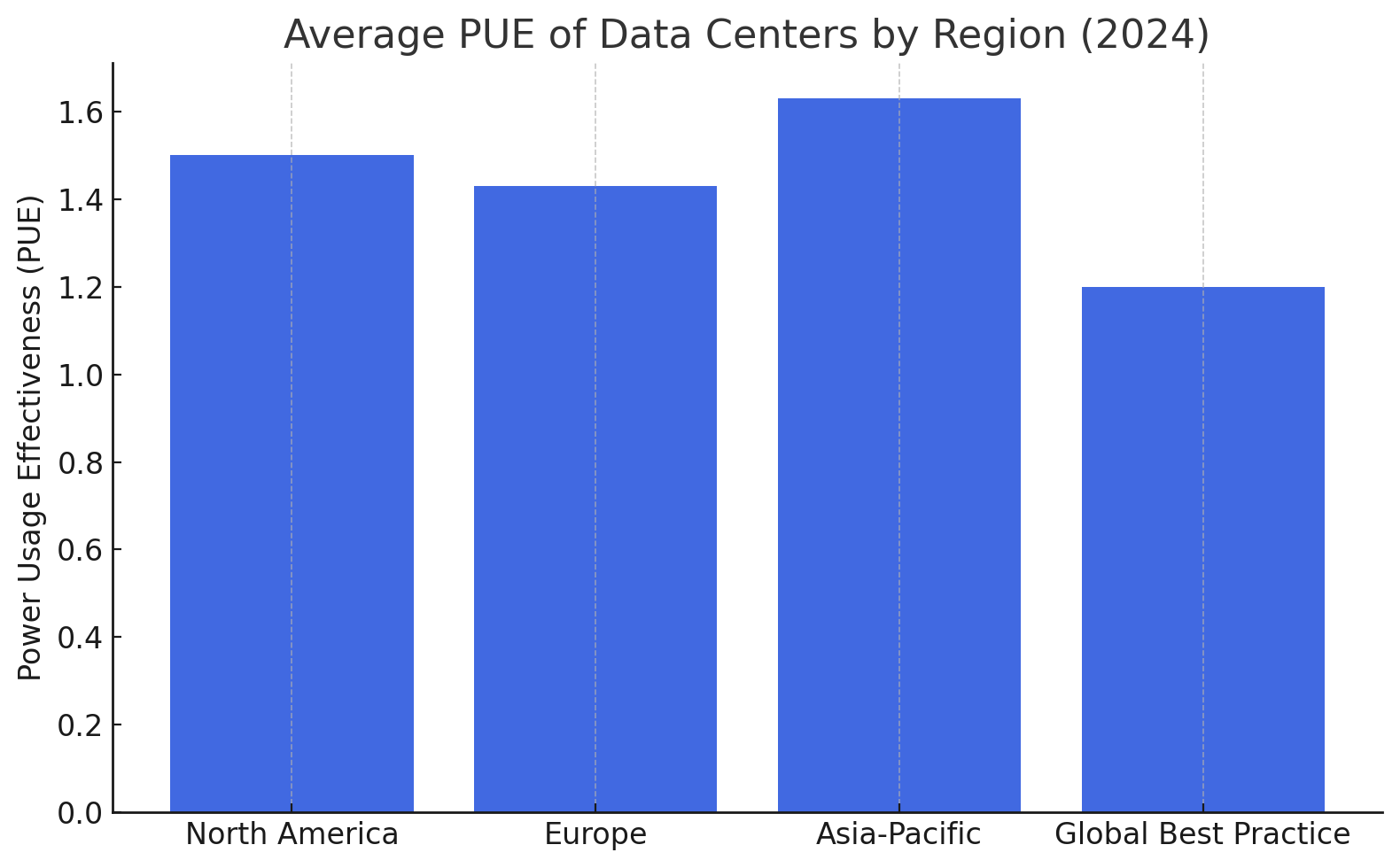
Region | Average PUE
--------------|-------------
North America | 1.50
Europe | 1.43
Asia-Pacific | 1.63
Global Best Practice | 1.20
Leading cloud providers like Google, AWS, and Microsoft have committed to 100% renewable-powered operations by 2030 or sooner.
Supply Chain Transparency and Rare Earth Materials
The IT industry relies heavily on rare earth elements (REEs) and minerals, often sourced from regions with environmental or labor risks. Transparency and traceability across the value chain are growing priorities under global ESG frameworks.
Strategic Shifts:
- Blockchain-based traceability for cobalt and lithium.
- Circular sourcing through device recycling programs.
- Supplier ESG scorecards and audits aligned with OECD standards.
Table: ESG Risks in IT Hardware Supply Chains
| Material | ESG Concern | Risk Mitigation Strategy |
|---|---|---|
| Cobalt | Child labor in mining | Certified conflict-free sourcing |
| Lithium | Water depletion in Chile | Closed-loop battery recycling |
| Tantalum | Armed conflict zones | Supply chain audits & traceability |
Regulations like the EU Battery Regulation and U.S. SEC conflict mineral rules are accelerating due diligence requirements.
Social Inclusion and Ethical AI
The social pillar of ESG is evolving in the IT sector, particularly in two areas: inclusion and algorithmic accountability. As AI and machine learning increasingly shape critical decisions, ethical guardrails are essential.
Areas of Action:
- DEI commitments and workforce diversification.
- Bias auditing in AI systems.
- Responsible AI governance frameworks and “AI Ethics Boards.”
Table: Diversity Metrics in Leading Tech Firms (2024)
| Company | Women in Workforce (%) | Underrepresented Minorities (%) |
|---|---|---|
| 34% | 11% | |
| Microsoft | 30% | 13% |
| Apple | 36% | 12% |
| Industry Avg. | 32% | 10% |
Investors and regulators alike are now expecting companies to not only quantify, but also govern, the social impact of their technologies.
ESG Governance and Digital Accountability
IT companies are facing mounting governance challenges, from data privacy to cybersecurity to misinformation. Robust ESG governance is emerging as a key indicator of corporate maturity and long-term viability.
Best Practices:
- ESG KPIs tied to executive compensation.
- Transparent lobbying and responsible tax strategies.
- ISO 27001 and SOC 2 for data governance and assurance.
Chart: ESG Risk Ratings by IT Subsector (2024)
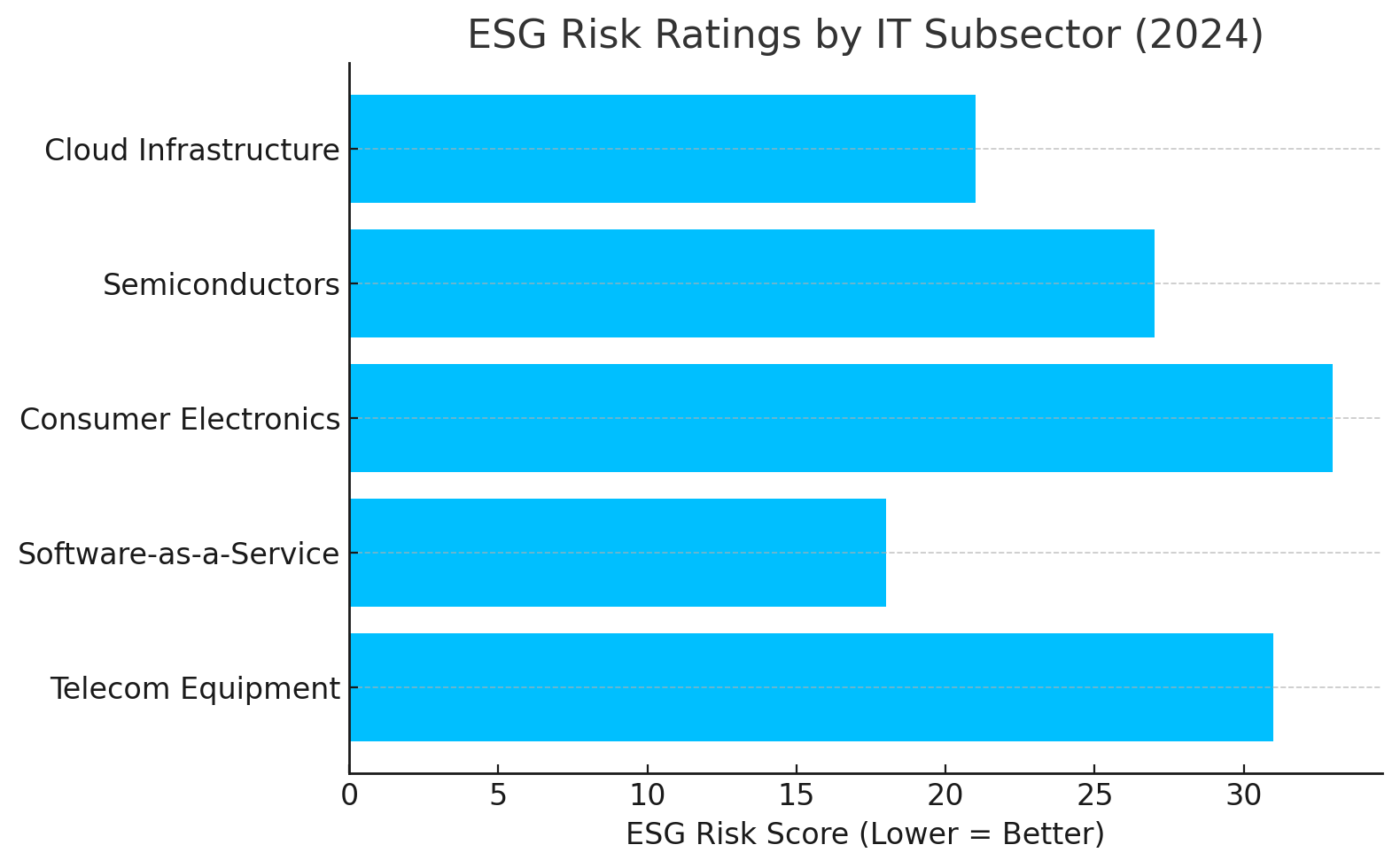
Subsector | ESG Risk Score (Lower = Better)
---------------------|--------------------------------
Cloud Infrastructure | 21
Semiconductors | 27
Consumer Electronics | 33
Software-as-a-Service| 18
Telecom Equipment | 31
Firms with strong governance systems are less likely to experience cybersecurity incidents, compliance failures, or reputational loss.
Standardized Reporting and Green IT Metrics
As ESG disclosure requirements tighten, especially under the EU’s CSRD and the ISSB standards, IT firms are investing in tools to quantify and communicate their ESG performance.
Key Developments:
- GHG Scope 3 emissions tracking (e.g. product use phase).
- Green coding initiatives for energy-efficient software.
- Integration of ESG into integrated financial reporting.
Table: ESG Reporting Framework Adoption by IT Companies (2024)
| Framework | Adoption Rate (%) |
|---|---|
| GRI | 62% |
| SASB | 58% |
| TCFD | 47% |
| ISSB-aligned | 34% |
| CSRD-prepared | 28% (EU companies only) |
The future of ESG in tech will depend not only on what companies do, but on how transparently and credibly they report it.
Conclusion: Toward Responsible Digital Leadership
The IT industry has long been a driver of innovation, but it now faces a new mandate: to lead not just technically, but ethically and sustainably. ESG is rapidly becoming the framework through which the public, investors, and regulators evaluate digital companies.
From low-carbon cloud computing to bias-free AI and traceable supply chains, the ESG transformation of IT is already underway. Companies that embrace this shift will not only reduce risk—they will build digital trust and long-term value.
Why Work with ASUENE Inc.?

ASUENE USA Inc., a subsidiary of Asuene Inc., is a key player in carbon accounting, offering a comprehensive platform that measures, reduces, and reports emissions, including Scope 1-3, with expertise in decarbonization. Asuene serves over 10,000 clients worldwide, providing an all-in-one solution that integrates GHG accounting, ESG supply chain management, a Carbon Credit exchange platform, and third-party verification.
ASUENE supports companies in achieving net-zero goals through advanced technology, consulting services, and an extensive network.

