- Article Summary
-
Introduction: Why the Apparel Industry Is in the Spotlight
The apparel industry is at the epicenter of a global transformation in corporate accountability. As concerns over environmental degradation and human rights abuses mount, regulatory bodies are stepping in to impose stricter controls. Nowhere is this more evident than in the European Union, where the recently adopted Corporate Sustainability Due Diligence Directive (CSDDD) introduces legally binding requirements for companies to identify, prevent, mitigate, and remediate adverse human rights and environmental impacts throughout their value chains.
But why focus on the apparel sector? This industry is among the most exposed and scrutinized under the new EU law. Its sprawling, multi-tiered supply chains often conceal severe labor violations, ecological damage, and opaque subcontracting practices. From cotton farms in Central Asia to dyeing mills in South Asia and garment factories in Southeast Asia, the risks are systemic and deeply embedded.
Moreover, the fashion industry is both consumer-facing and fast-moving, which makes it especially vulnerable to reputational risk. With sustainability and ethics rising on consumer and investor agendas, apparel brands are under immense pressure to clean up their supply chains. EU regulators have taken note. Textiles and fashion are explicitly targeted in the EU Strategy for Sustainable and Circular Textiles.
This blog explores how the CSDDD affects apparel companies, where the greatest supply chain risks lie, and how brands can turn transparency into a strategic advantage.
What the EU Due Diligence Laws Require
The Corporate Sustainability Due Diligence Directive (CSDDD), adopted in 2024, imposes legal obligations on both EU-based and non-EU companies operating in the EU market. Apparel companies with over 1,000 employees and annual revenues exceeding €450 million are squarely within its scope. Non-EU firms meeting the same revenue threshold from EU markets are also covered.
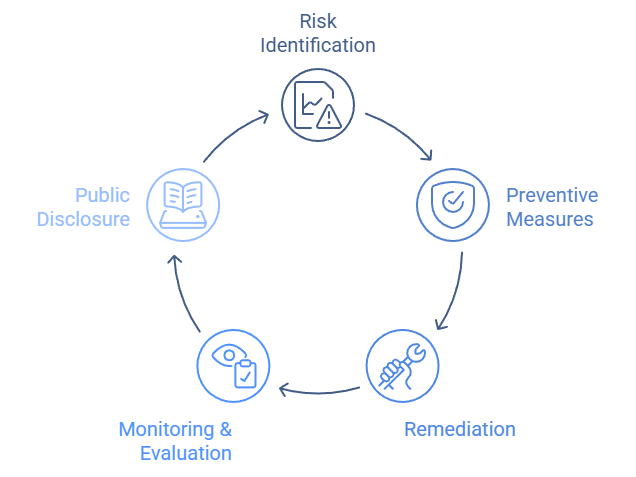
Key legal requirements include:
| Requirement | Explanation |
|---|---|
| Risk Identification and Assessment | Evaluate potential human rights abuses and environmental risks across all tiers. |
| Preventive Measures | Implement policies and procedures to avoid or reduce negative impacts. |
| Remediation | Offer remedies to individuals or communities harmed by business activities. |
| Monitoring and Evaluation | Continuously assess and improve due diligence practices. |
| Public Disclosure | Report annually on due diligence efforts, findings, and outcomes. |
This directive aligns with the UN Guiding Principles on Business and Human Rights and the OECD Guidelines for Multinational Enterprises, making it part of a broader shift toward mandatory ESG compliance.
Exposing Risks from Tier 1 to Tier 4 in the Apparel Supply Chain
The apparel supply chain is one of the most fragmented and opaque in the global economy. To comply with the CSDDD, brands must address not only their direct (Tier 1) suppliers but also upstream partners in Tier 2, Tier 3, and Tier 4, where raw material extraction or cultivation takes place.
Supply Chain Tiers Explained:
| Tier | Stage | Examples |
| Tier 1 | Final assembly | Cut-and-sew factories |
| Tier 2 | Material processing | Dyeing, printing, washing facilities |
| Tier 3 | Fabric and yarn production | Spinning mills, weaving units |
| Tier 4 | Raw material extraction or cultivation | Cotton farms, sheep herders, petrochemical suppliers |
Major ESG Risks by Tier:
Tier 1 (Final garment assembly):
- Labor risks: Subcontracting that obscures wage violations, excessive overtime, safety hazards, and worker harassment.
- Transparency risks: Limited traceability due to unauthorized subcontracting and poor audit documentation.
Tier 2 (Material processing):
- Labor risks: Exposure to toxic chemicals, poor workplace ventilation, and limited protective equipment.
- Environmental risks: Contaminated wastewater, dye runoff polluting local waterways, high emissions from processing equipment.
Tier 3 (Fabric and yarn production):
- Labor risks: Unsafe working conditions, long hours with insufficient pay, and low union representation.
- Environmental risks: High energy consumption, fiber dust and indoor air pollution, unregulated chemical treatments.
Tier 4 (Raw material cultivation or extraction):
- Human rights risks: Forced labor in cotton farming, child labor in cotton picking, informal labor with no contracts or protections.
- Environmental risks: Excessive water use for cotton, pesticide overuse harming ecosystems, deforestation for cellulose-based fibers, pollution from petroleum extraction.
Due diligence must therefore be full-spectrum, covering actors that are often invisible to brands. This means moving beyond audit checklists and investing in technologies and partnerships that enable traceability from the cotton field to the retail shelf.

From Compliance to Competitive Advantage
While regulatory pressure is the primary driver, transparency can also become a strategic asset. Supply chain visibility helps companies build brand trust, improve operational efficiency, and enhance ESG performance.
Technology Enablers:
- Blockchain: For unchangeable traceability records
- DNA tagging: To verify fiber origin
- Digital Product Passports: Designed to communicate sustainability data across the value chain
Table 1: Strategic Benefits of Supply Chain Transparency
| Benefit | Description |
| Consumer Trust | Informed buyers prefer brands with traceable, ethical sourcing practices |
| Investor Confidence | ESG metrics influence access to capital and portfolio inclusion |
| Operational Resilience | Early risk detection and diversified sourcing reduce disruption |
| Legal Risk Reduction | Proactive compliance reduces exposure to lawsuits and penalties |
| Innovation Catalyst | Transparency often accelerates circularity, material innovation, and R&D |
A Roadmap for Compliance and Leadership in the Apparel Sector
To meet EU requirements and lead in sustainability, apparel brands should follow a structured implementation path. Here is a proposed roadmap:
1. Gap & Risk Assessment
Map all supply chain tiers, identify high-risk regions and suppliers, and assess existing compliance tools.
2. Supplier Engagement
Educate and support suppliers on ESG standards, provide training, and co-invest in improvements.
3. Traceability Systems
Deploy digital tools (e.g., blockchain, QR codes, databases) to track products through all tiers.
4. Worker Grievance Mechanisms
Establish safe, anonymous channels for workers to report issues, especially in lower-tier factories and farms.
5. Transparent Reporting
Publish annual due diligence reports, aligned with EU disclosure rules and verified by independent bodies.
In addition, brands should align with global frameworks like the Higg Index, SLCP, and Textile Exchange standards to bolster credibility and comparability.
Conclusion: A Turning Point for Fashion and Accountability
The apparel industry is on the front lines of a new era of supply chain regulation and scrutiny. The EU’s due diligence laws signal that transparency is no longer optional. It is a legal, ethical, and strategic necessity.
Apparel companies that act now to build traceable, responsible supply chains will not only ensure compliance but also differentiate themselves in a competitive, values-driven market. The time for reactive, surface-level audits is over. What comes next is systemic transformation driven by law, but ultimately powered by leadership and innovation.
Why Work with ASUENE Inc.?
Asuene is a key player in carbon accounting, offering a comprehensive platform that measures, reduces, and reports emissions. Asuene serves over 10,000 clients worldwide, providing an all-in-one solution that integrates GHG accounting, ESG supply chain management, a Carbon Credit exchange platform, and third-party verification.
ASUENE supports companies in achieving net-zero goals through advanced technology, consulting services, and an extensive network.


