- Article Summary
-
The European Union’s Circular Economy Action Plan (CEAP) is a cornerstone of the European Green Deal and a roadmap for achieving climate neutrality by 2050. CEAP is not just about recycling more—it’s about redefining growth models through smarter design, sustainable production, and responsible consumption. The updated CEAP 2.0, launched in 2020, emphasizes systemic transformation across product lifecycles, industrial value chains, and economic sectors.
This article explores how CEAP policies are shaping business strategies, ESG reporting, and innovation in key sectors. It also highlights implementation progress, regulatory instruments, and the role of circular metrics in corporate performance.
CEAP in Focus: Policy Pillars and Priority Sectors
The CEAP introduces legislative and non-legislative measures under four main pillars:
- Sustainable product design: Embodied in ESPR and sectoral eco-design.
- Circular production processes: Encouraging resource recovery and clean production.
- Sustainable consumption: Boosting durability, repair, reuse, and transparency.
- Waste reduction and management: Targeted efforts to minimize landfill, promote separate collection, and standardize labeling.
Priority sectors include:
- Electronics and ICT
- Textiles and apparel
- Construction and buildings
- Batteries and vehicles
- Packaging and plastics
Table: CEAP Priority Sectors and Key Policy Actions
| Sector | Policy Tools | Circular Focus |
|---|---|---|
| Electronics | ESPR, Right to Repair | Reparability, reuse |
| Textiles | EU Strategy for Sustainable Textiles | Design, EPR, recyclability |
| Construction | EU Green Deal Renovation Wave | Material reuse, CO2 reduction |
| Batteries | Battery Regulation | Lifecycle data, recycling |
| Packaging | PPWR | Reuse targets, recyclability |
Circular Economy and Corporate ESG Strategy
CEAP is accelerating the shift from linear business models to circular value creation, with direct implications for ESG performance:
- Scope 3 emissions: Circular design can significantly reduce value chain emissions.
- Materiality analysis: CEAP-aligned sectors face heightened regulatory and investor scrutiny.
- Reporting standards: The CSRD mandates disclosure of circular metrics (e.g., material intensity, waste diversion rates).
- Sustainable finance: EU Taxonomy recognizes circular activities as eligible green investments.
Leading companies are integrating CEAP goals into:
- Product innovation (e.g., modular smartphones, compostable textiles)
- Supplier engagement (e.g., closed-loop procurement models)
- End-of-life programs (e.g., take-back schemes, digital material passports)

Measuring Circularity: Metrics That Matter
The effectiveness of circular transitions depends on robust measurement. Key indicators include:
- Material Circularity Indicator (MCI): Ratio of virgin to secondary materials.
- Product lifespan and reuse rate
- Waste-to-resource conversion rate
- CO2 savings through circular practices
Graph: Adoption of Circular Metrics in Corporate ESG Reports (2018–2024)
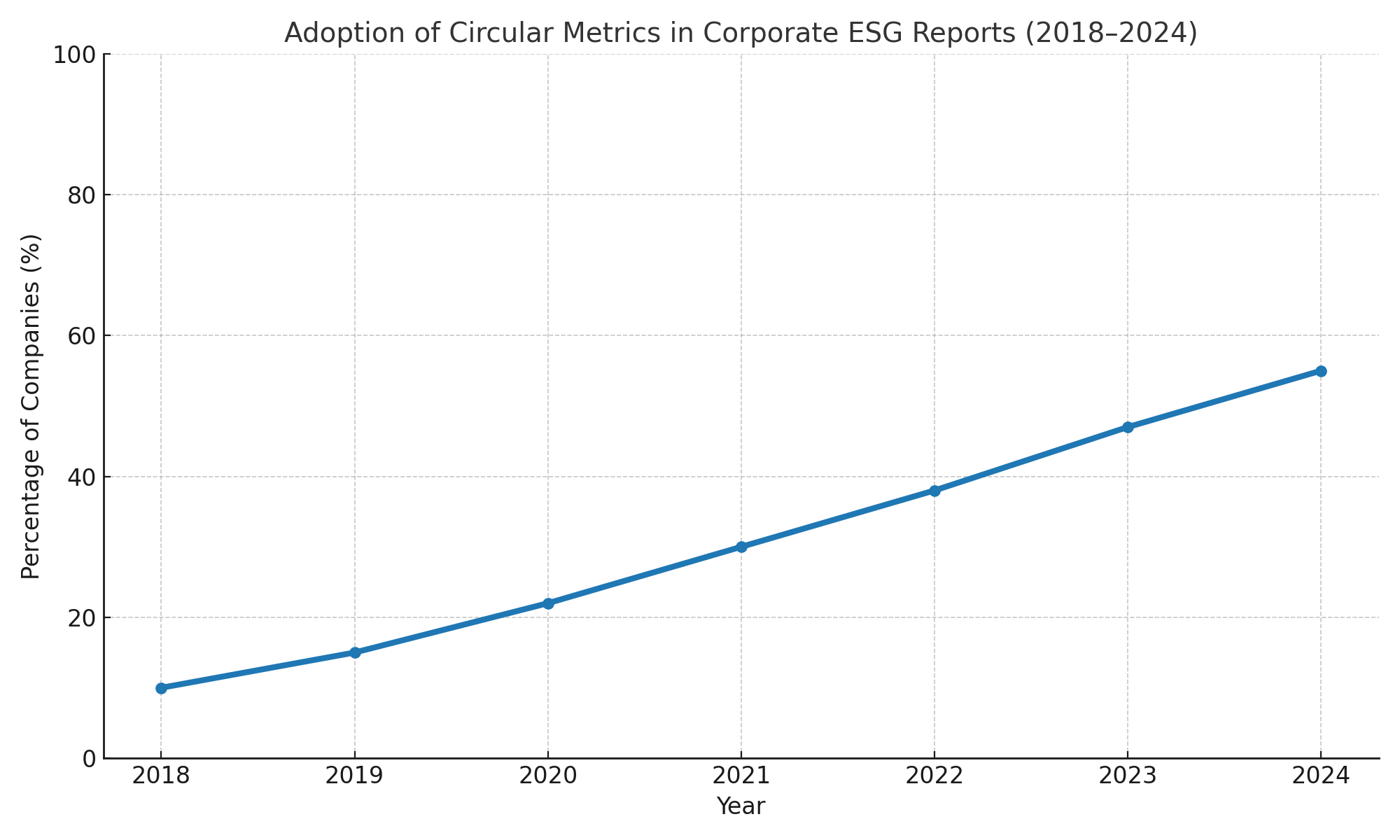
Companies are increasingly using LCA, digital twins, and blockchain traceability to quantify product impacts and demonstrate compliance with CEAP principles.
Looking Ahead: Scaling Circular Innovation
The CEAP provides both regulatory push and market pull for innovation. To scale circular solutions, the EU is:
- Expanding eco-modulation in Extended Producer Responsibility (EPR) fees
- Funding industrial symbiosis and waste-to-X pilots through Horizon Europe
- Establishing product-specific targets and bans (e.g., microplastics, greenwashing claims)
Public-private partnerships, especially in cross-sectoral areas like construction and textiles, are key to success. SMEs are being supported through Digital Innovation Hubs and technical assistance.
Conclusion
The CEAP is reshaping the European economy toward resilience, resource efficiency, and climate alignment. For businesses, it is both a regulatory framework and a competitive blueprint.
By embedding circular thinking into product strategy, operations, and reporting, companies can lead in the next generation of sustainable business. Circularity is no longer a niche concept—it is a central pillar of ESG performance and future-ready innovation.
Why Work with ASUENE Inc.?
Asuene is a key player in carbon accounting, offering a comprehensive platform that measures, reduces, and reports emissions, including Scope 1-3, with expertise in decarbonization. Asuene serves over 10,000 clients worldwide, providing an all-in-one solution that integrates GHG accounting, ESG supply chain management, a Carbon Credit exchange platform, and third-party verification.
ASUENE supports companies in achieving net-zero goals through advanced technology, consulting services, and an extensive network.


