- Article Summary
-
Introduction: Cement’s Decarbonization Moment
The Global Cement and Concrete Association (GCCA) has introduced a new membership category that brings together innovators and partners from across the value chain. This initiative is designed to accelerate the cement and concrete sector’s transition toward net zero and signals a major shift in how the industry collaborates on sustainability.
Cement and concrete, the materials that literally build our cities and infrastructure, are also among the world’s biggest climate challenges, responsible for roughly 7% of global CO2 emissions. The sector’s carbon intensity has made it one of the six commodities covered under the EU’s Carbon Border Adjustment Mechanism (CBAM), alongside steel, aluminum, fertilizer, electricity, and hydrogen. This inclusion means cement is now under intense scrutiny not only from Europe but from regulators and investors worldwide, all demanding stronger decarbonization strategies and transparent emissions data.
The GCCA’s initiative and other emerging global alliances represent a new model of collaborative decarbonization for hard-to-abate industries, showing how data-driven cooperation will be key to cement’s low-carbon future.
A New Membership Model for a New Era
The GCCA’s new membership category marks a significant shift in how the cement and concrete industry approaches sustainability. The program is open to suppliers, technology firms, equipment manufacturers, start-ups, and other organizations that are working to cut the sector’s carbon footprint. The goal is to foster cross-industry cooperation, accelerate the deployment of innovative technologies, and build a unified roadmap to net zero by 2050.
This model reflects a global trend where collaboration replaces competition in tackling climate challenges. By aligning the interests of multiple players across the value chain, the GCCA aims to ensure that low-carbon solutions are developed, tested, and scaled faster than ever before.
| Stakeholder Type | Contribution to Net Zero Cement |
|---|---|
| Energy Companies | Supply renewable energy and low-carbon fuels |
| Technology Firms | Develop efficiency and carbon capture solutions |
| Equipment Manufacturers | Upgrade kilns and machinery to reduce emissions |
| Start-ups | Introduce innovative materials and digital tracking tools |
| Construction Firms | Drive demand for verified low-carbon concrete |
Why Cement’s Emissions Are So Hard to Cut
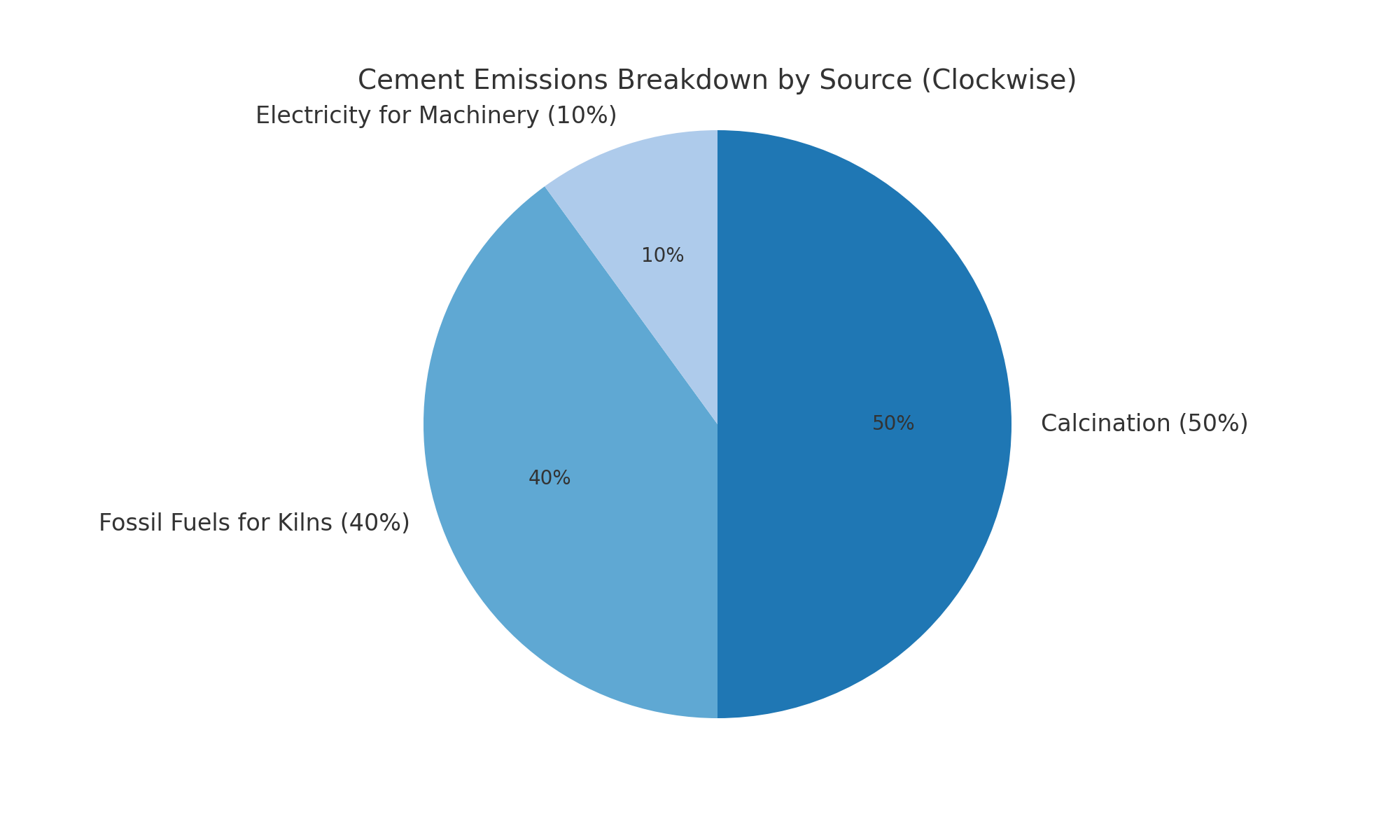
Cement production is one of the most complex industrial processes to decarbonize. Around 50% of its emissions come from the chemical reactions involved in converting limestone into clinker, while about 40% arise from the combustion of fuels to heat the kilns. 10% are from electricity to power additional machinery. The sector’s dependency on high temperatures and carbon-intensive materials makes deep decarbonization difficult.
Emerging solutions include carbon capture and storage (CCS), low-clinker or alternative binders, renewable-powered kilns, green hydrogen use, and the circular recycling of materials. However, innovation alone is not enough. True progress requires alignment across supply chains, from raw material suppliers to construction clients.
Collaboration as the Core of Decarbonization
Cross-sector collaboration is essential to overcoming cement’s climate challenge. The energy sector can provide renewable power and alternative fuels. The construction industry can prioritize sustainable procurement and create demand for verified low-carbon materials. Financial institutions can enable transition finance, while technology providers can deliver the tools needed to measure and manage progress.
Several partnerships have already emerged under the GCCA and other global frameworks, proving that cooperation can unlock faster innovation. A blue-themed diagram showing the interconnected value chain, from raw materials to end-use in construction, can demonstrate how every actor plays a role in achieving net zero.
This model of shared responsibility could become a template for other heavy industries such as steel and chemicals, where collaboration will be equally critical to meet global carbon goals.

Data and Digitalization: The Hidden Accelerator
Digital platforms are becoming the hidden accelerator of decarbonization. Accurate lifecycle emissions tracking and Scope 3 management are now fundamental requirements for companies operating under international climate frameworks. Without transparent data, progress cannot be measured or trusted.
ASUENE’s data-driven solutions empower industries to measure, visualize, and reduce their carbon impact across the entire supply chain. By integrating lifecycle assessment tools and real-time data analysis, companies can identify inefficiencies, validate emission reductions, and share progress with stakeholders.
Conclusion: Building the Foundation for a Net Zero Industry
The cement sector’s net zero journey symbolizes a broader global shift toward collective responsibility in climate action. The GCCA’s inclusive membership model demonstrates how alliances can break down silos and unite industries around a shared decarbonization goal.
Data, transparency, and collaboration will define how quickly and equitably this transformation occurs. If cement, one of the hardest sectors to decarbonize, can change course through cooperation, then other industries can follow. By leveraging platforms such as ASUENE, companies can strengthen their data-driven strategies and join the global effort to build a sustainable, low-carbon future.
Why Work with ASUENE Inc.?
ASUENE is a key player in carbon accounting, offering a comprehensive platform that measures, reduces, and reports emissions. ASUENE serves over 10,000 clients worldwide, providing an all-in-one solution that integrates GHG accounting, ESG supply chain management, a Carbon Credit exchange platform, and third-party verification.
ASUENE supports companies in achieving net-zero goals through advanced technology, consulting services, and an extensive network.


