- Article Summary
-
Introduction
As stakeholders increasingly demand transparency on environmental impacts, companies are turning to life cycle assessment (LCA) to quantify the carbon footprint of their products. A product’s environmental performance—from raw material extraction through use and end-of-life—has become central to ESG reporting, consumer trust, and regulatory compliance. Frameworks such as the Greenhouse Gas Protocol, ISO 14040/44, and CDP now emphasize product-level emissions as a material aspect of corporate climate impact.
This article explores the role of LCA in carbon impact assessment, how it aligns with disclosure requirements under frameworks like TCFD and CDP, and how companies can use LCA results to shape competitive and compliant carbon disclosure strategies.
The Role of LCA in Understanding Carbon Footprint
Life cycle assessment is a standardized methodology for evaluating environmental impacts associated with all stages of a product’s life. It provides a granular view of emissions across:
- Raw material extraction (cradle)
- Manufacturing and production
- Distribution and logistics
- Product use phase
- End-of-life (grave)
For carbon impact specifically, LCA calculates the total greenhouse gas emissions—expressed in CO2-equivalent—across these stages. This helps companies identify emissions hotspots and prioritize decarbonization interventions.
Figure 1: Generic Product Lifecycle Emissions Distribution (Illustrative %)
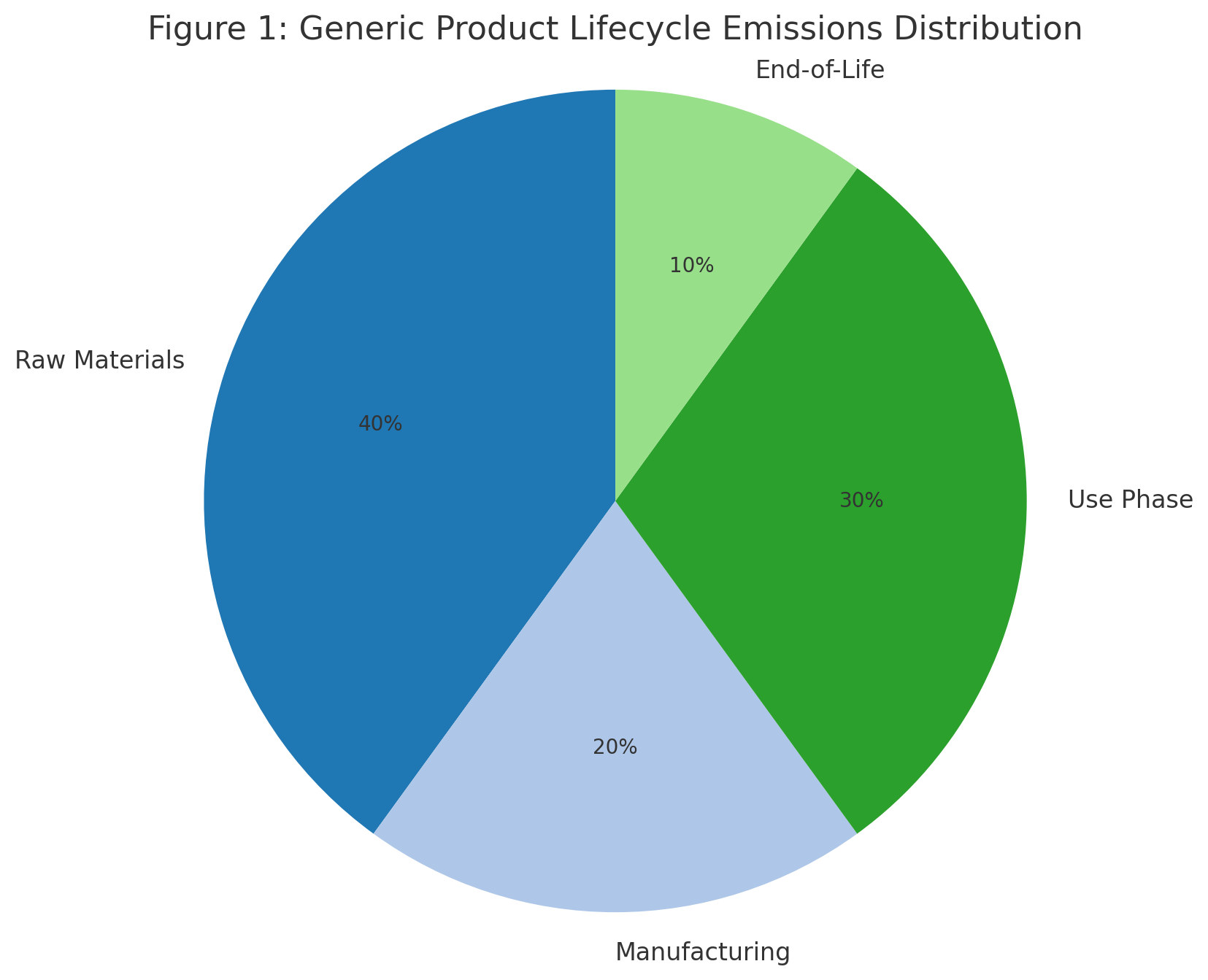
| Lifecycle Stage | Typical Share of Emissions |
|---|---|
| Raw Materials | 40% |
| Manufacturing | 20% |
| Use Phase | 30% |
| End-of-Life | 10% |
LCA Standards and Integration with ESG Frameworks
Multiple standards govern the conduct and reporting of LCA. The most widely used are:
- ISO 14040/14044: Methodological guidance on LCA.
- GHG Protocol Product Standard: Focuses on product life-cycle GHG emissions.
- Environmental Product Declarations (EPDs): Verified LCA summaries used in B2B markets.
- CDP Supply Chain & Products: Requires product-level emissions disclosure from suppliers.
These frameworks support the integration of LCA insights into broader ESG disclosure, particularly under TCFD’s Metrics & Targets and CDP’s emissions categories (Scope 3 – Category 11: Use of sold products).

Digital Tools and Data Management for Scalable LCA
Conducting high-quality LCA can be resource-intensive. To scale assessment across product portfolios, many companies are adopting digital platforms and datasets:
- Software: SimaPro, GaBi, OpenLCA—LCA modeling and impact calculation.
- Databases: ecoinvent, GaBi DB, ELCD—life cycle inventory (LCI) data.
- Automation: Integration with PLM (Product Lifecycle Management) or ERP systems to auto-calculate impacts based on bill-of-materials.
Figure 2: Examples of Digital Tools for Product-Level Carbon Assessment
| Tool | Function | Best Use Case |
| SimaPro | Full LCA modeling | Academic & R&D |
| GaBi | Enterprise-grade LCA | Product portfolio analysis |
| OpenLCA | Open-source LCA | SMEs and pilots |
| ecoinvent | Inventory database | Standardized emission data |
Disclosure Strategy and Market Communication
Effective communication of LCA findings is essential for both compliance and competitive differentiation. Key approaches include:
- Product Carbon Footprint (PCF) Labeling: Transparency to consumers, especially in electronics, apparel, and food sectors.
- EPDs: Used in procurement, particularly in construction, infrastructure, and public tenders.
- CDP & TCFD Reporting: Integrating LCA-based insights into annual ESG or climate reports.
- SBTi Alignment: Using LCA data to define Scope 3 product use phase targets.
Figure 3: LCA Integration Points in ESG and Climate Disclosure
| Platform | LCA Use Case | Benefit |
| CDP | Scope 3 Category 11 reporting | Investor transparency |
| TCFD | Metrics & Targets disclosure | Climate risk readiness |
| SBTi | Product emissions baseline | Science-based target setting |
| EPD | B2B marketing, public tenders | Market access & trust |
Conclusion
As ESG and climate regulations mature, companies that understand and disclose the full carbon lifecycle of their products gain strategic advantage. LCA not only satisfies growing stakeholder demand for transparency, but also enables smarter product design, regulatory compliance, and value chain decarbonization. By embedding LCA into ESG reporting systems and leveraging digital tools, firms can turn data into action—and emissions into opportunity.
Why Work with ASUENE Inc.?
Asuene is a key player in carbon accounting, offering a comprehensive platform that measures, reduces, and reports emissions, including Scope 1-3, with expertise in decarbonization. Asuene serves over 10,000 clients worldwide, providing an all-in-one solution that integrates GHG accounting, ESG supply chain management, a Carbon Credit exchange platform, and third-party verification.
ASUENE supports companies in achieving net-zero goals through advanced technology, consulting services, and an extensive network.


