- Article Summary
-
Introduction
Chemicals are essential to modern life but pose risks to human health and the environment if improperly managed. With regulatory pressure mounting—from substance-level controls like REACH and PFAS restrictions to systemic ESG reporting like the CSRD—companies can no longer treat compliance and sustainability as separate domains. Understanding their interconnections can drive innovation, reduce risk, and unlock competitive advantage.
What is REACH?

Definition and Purpose
REACH stands for Registration, Evaluation, Authorisation, and Restriction of Chemicals. Enacted in 2007 and administered by the European Chemicals Agency (ECHA), REACH aims to:
- Protect human health and the environment.
- Enhance the competitiveness of the EU chemicals industry.
Scope and Impact
REACH applies to over 30,000 substances and affects companies across industries from agriculture to cosmetics. Any company producing or importing more than one ton of a chemical annually must register it with detailed safety data.
Key Components
- Registration: Submission of safety data to ECHA.
- Evaluation: Review of submitted data.
- Authorisation: Control over substances of very high concern (SVHC).
- Restriction: Prohibition or limitation of hazardous substances.
What are PFAS?
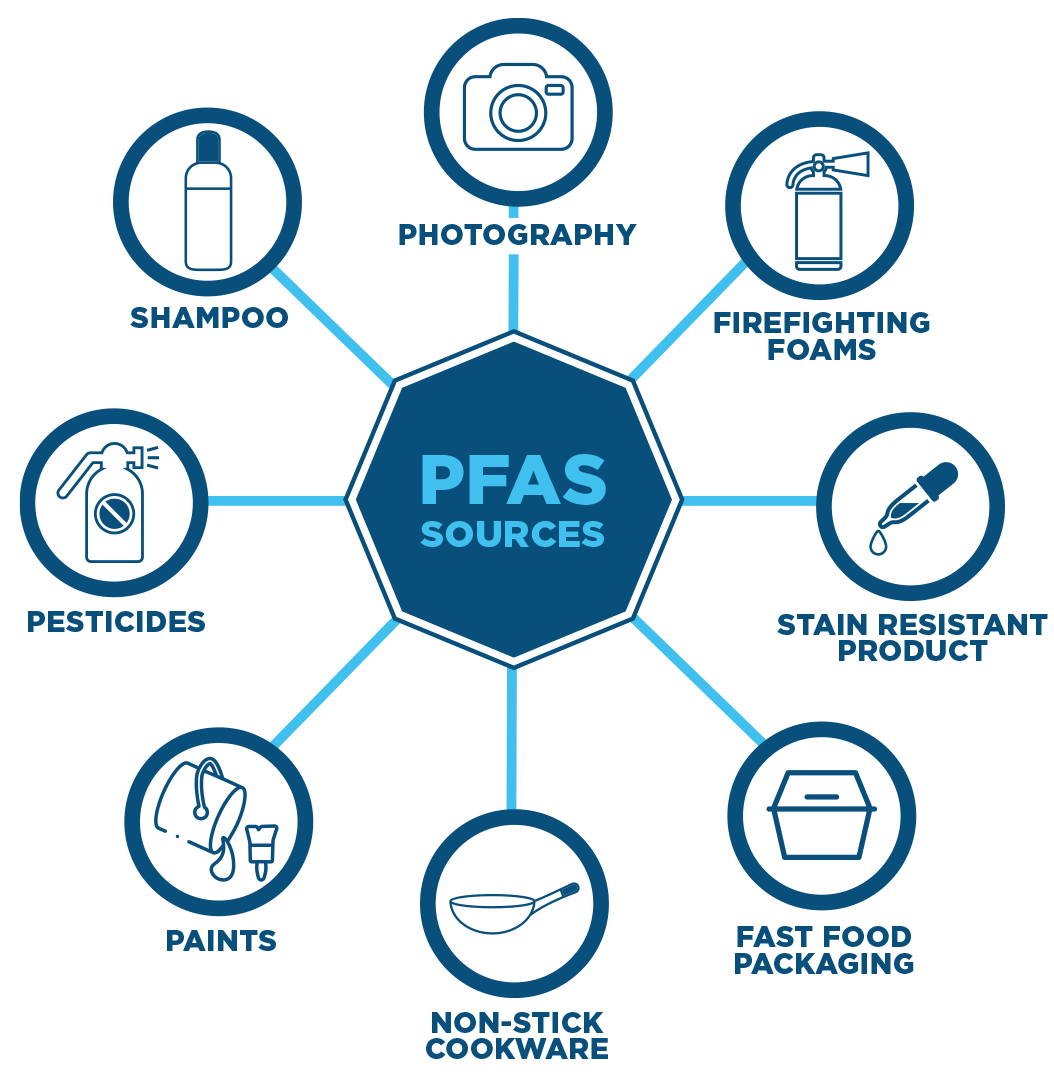
Definition and Characteristics : PFAS (per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances) are over 10,000 synthetic chemicals used since the 1950s. Their carbon-fluorine bonds make them extremely resistant to breakdown, hence the name “forever chemicals.”
Common Use:Non-stick cookware, Waterproof clothing, Firefighting foams and Food packaging
Health and Environmental Risks:
- Linked to cancer, immune disorders, and developmental toxicity.
- Persist in water and soil, with high cleanup costs.
REACH and PFAS: Regulatory Intersection
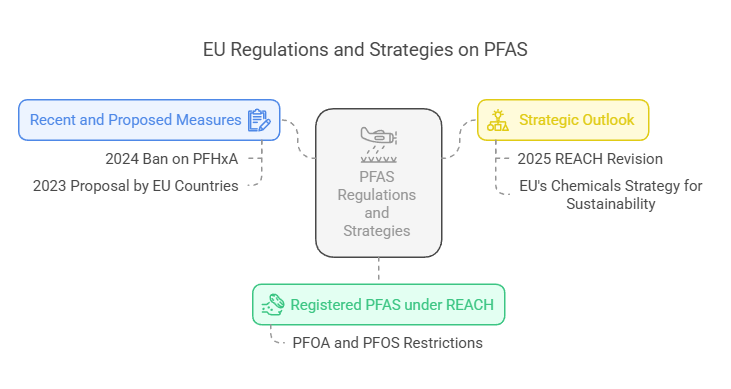
PFAS Under REACH
At least 531 PFAS are registered under REACH, though many registrations lack full persistence, bioaccumulation, and toxicity data. Substances like PFOA and PFOS are already restricted under REACH and the Persistent Organic Pollutants (POPs) Regulation.
Recent and Proposed Measures
- 2024: Ban on PFHxA in textiles and food packaging.
- 2023: Five EU countries proposed restricting all PFAS (~10,000 substances).
- Proposed full bans with 5–12 year derogations for essential uses.
Strategic Outlook: The 2025 REACH revision and the EU’s Chemicals Strategy for Sustainability aim to phase out non-essential PFAS, reduce authorization complexity, and enhance hazard data collection.
Connecting REACH & PFAS with Environmental Reporting
As regulations expand, companies must not only comply with substance restrictions but also disclose their broader environmental impact. Here’s how these frameworks connect:
Alignment of REACH and PFAS with Sustainability Disclosure
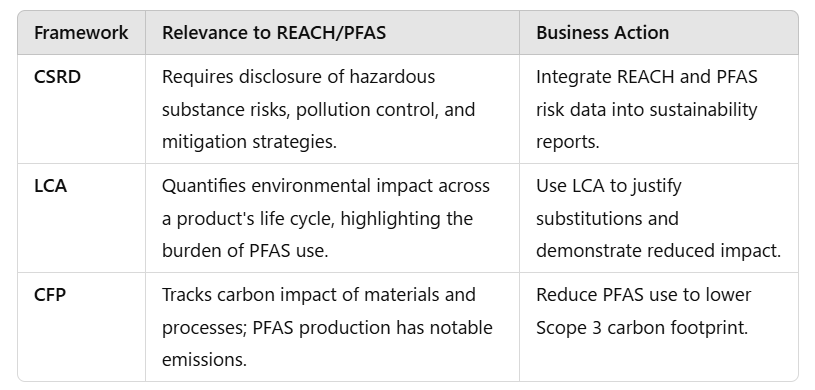
Practical Integration Strategies
- Centralize substance data to feed both compliance and ESG reporting.
- Engage suppliers on REACH/PFAS status and Scope 3 emissions.
- Prioritize PFAS-free product design in R&D.
- Use LCA and CFP outputs in CSRD narrative disclosures.
Challenges and Opportunities for Manufacturers
Challenges
- Navigating complex substance-level and system-level regulations.
- Managing growing data requirements across REACH, CSRD, and LCA.
- Maintaining supply chain visibility and compliance.
Opportunities
- Compliance as ESG Strategy: Link REACH and PFAS measures with broader sustainability goals.
- Technology Investment: Use ISO 14001 systems and digital LCA tools to reduce reporting burdens.
- Innovation Catalyst: Replace high-impact substances through green chemistry innovation.
Turning Compliance into Competitive Edge
As the EU strengthens its stance on environmental protection, REACH and PFAS regulations are converging with broader ESG frameworks like CSRD and LCA. For chemical manufacturers, this convergence is not a burden but a strategic opportunity.
By embedding compliance into sustainability reporting and innovation processes, companies can:
- Mitigate regulatory and reputational risk.
- Lower environmental impact.
- Differentiate through transparency and safer products.
Staying ahead means not just avoiding fines—but becoming a leader in sustainable transformation.
Stay tuned for future posts as we continue exploring how ESG, compliance, and innovation intersect in the chemical sector.
Why Partner with ASUENE USA Inc.?

To navigate the complex climate disclosure requirements, appropriate tools and expertise are essential. This is where ASUENE USA Inc. comes in.
Carbon Accounting: Our advanced software solutions automate emissions tracking across Scopes 1, 2, and 3, integrating with existing ERP systems to reduce manual data entry errors. Proprietary algorithms align with GHG Protocol standards, ensuring compliance with ESG reporting mandates.
Third-Party Verification: ASUENE’s network of accredited auditors provides ISO 14064-compliant verification services, a critical step for companies seeking to validate their disclosures.
By partnering with ASUENE USA, businesses can transform regulatory obligations into strategic advantages, enhancing sustainability performance while minimizing compliance costs.
So, why not partner with us to streamline your reporting and environmental efforts? Let ASUENE USA Inc. help you stay ahead of the curve while making a positive impact on both your business and the planet.
Talk to us today for your sustainable transformation!
Download our latest White Paper

